Essential Components of a Cybersecurity Framework
Learn about the core components of a cybersecurity framework and how they are designed to protect your organization from emerging digital threats.

From my experience, a strong cybersecurity framework is essential for protecting important data and systems from constantly changing threats. A good framework includes key areas like managing risks, securing networks, protecting data, and monitoring for threats. By putting this in place, businesses can better defend themselves and keep their data and operations safe from attacks.
Understanding the Importance of a Cybersecurity Framework
A cybersecurity framework is essential for managing security risks in an organized way. It provides a structured approach to protecting sensitive data and maintaining the continuity of business operations. By outlining processes for both preventing and responding to cyber threats, a cybersecurity framework helps ensure that organizations are prepared to handle risks and mitigate potential damages.
With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, traditional security methods are no longer enough. A comprehensive framework provides businesses with proactive measures to assess, address, and minimize risks before they lead to significant breaches.
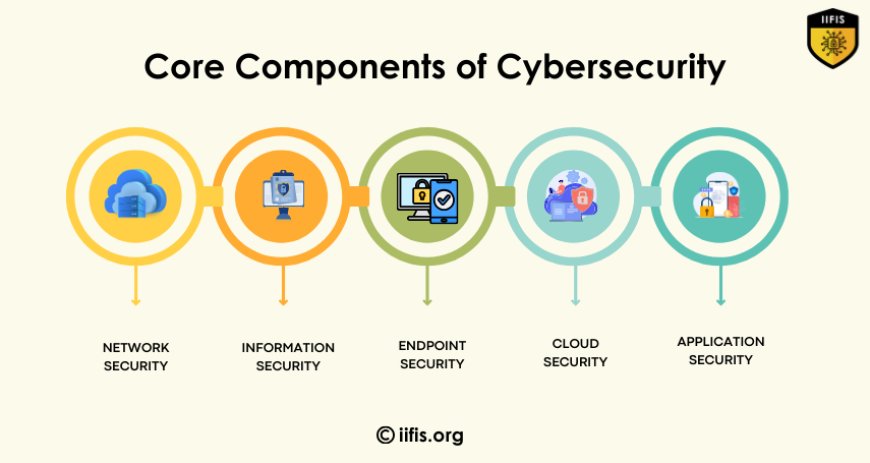
Core Components of Cybersecurity
-
Firewalls: Block unauthorized access between internal and external networks.
-
IDS/IPS: Detect and prevent malicious network activity.
-
VPNs: Ensure secure remote access with encrypted communication.
-
Network Segmentation: Isolate critical systems to reduce the attack surface.
-
Data encryption: converts sensitive data into unreadable text.
-
Data classification: categorizes data based on sensitivity.
-
DLP: Prevents unauthorized data transfer.
-
Backup & Disaster Recovery: Ensures data availability during incidents.
3. Endpoint Security
-
Antivirus/Anti-malware: Detects and removes malicious software.
-
EDR: Monitors and responds to suspicious endpoint activities.
-
MDM: Secures mobile devices within the organization.
4. Cloud Security
-
CASB: Monitors cloud apps for unauthorized access.
-
Shared Responsibility Model: Defines security responsibilities between provider and user.
-
Encryption: Secures data in the cloud.
5. Application Security
-
Focuses on securing applications from vulnerabilities and cyberattacks through secure coding practices and regular testing.
Risk Management: Identifying and Prioritizing Threats
Effective risk management is one of the primary components of cybersecurity that helps organizations identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential threats. It focuses on understanding which vulnerabilities pose the greatest risk to the organization and implementing strategies to address those threats.
The process involves several key steps:
-
Identifying threats: recognize potential risks, including cyberattacks, insider threats, and hardware malfunctions.
-
Assessing vulnerabilities: Evaluate how vulnerable the organization is to each threat, considering both internal and external factors.
-
Prioritizing risks: Based on the severity and likelihood of the risk, prioritize which threats to address first.
Risk management ensures that businesses are not only prepared for possible attacks but also able to respond quickly, minimizing potential damage.
Governance, Policies, and Procedures: Creating a Security Culture
Governance is a vital component in building a robust cybersecurity framework. It refers to the policies and procedures that guide an organization’s approach to security and ensures that everyone is on the same page when it comes to safeguarding sensitive information.
A strong governance model includes:
-
Clear cybersecurity policies: These policies define how employees should handle data and access company resources.
-
Defined roles and responsibilities: Ensuring that each employee understands their cybersecurity duties, from top executives to entry-level staff.
-
Compliance: Ensuring adherence to industry regulations and laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS to avoid legal penalties and security risks.
By establishing these governance elements, organizations can instill a culture of security awareness, where everyone understands their role in protecting the business.
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controlling Who Can Access What
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is another key component of cybersecurity that helps control user access to systems and data. IAM ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized breaches.
Key elements of IAM include:
-
User authentication: verifying the identity of users through methods like passwords, biometrics, and two-factor authentication.
-
Access controls: Limiting what users can see and do within a system, based on their role and needs.
-
Regular audits: continuously monitoring and reviewing access privileges to ensure that employees only have access to the resources they need.
With the rise of remote work and cloud-based technologies, IAM systems are essential to prevent unauthorized access and maintain control over corporate data.
Security Monitoring and Incident Response: Detecting and Responding to Threats
A proactive approach to detecting and responding to cyber threats is critical for maintaining a secure environment. Security monitoring allows organizations to identify suspicious activities in real time, while an effective incident response plan ensures quick recovery in case of a breach.
Security monitoring includes:
-
Intrusion detection systems (IDS): These tools monitor network traffic and systems for signs of potential attacks.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM platforms collect and analyze data from various sources to identify potential threats and security incidents.
Once an incident is detected, the incident response plan should be activated. This plan includes:
-
Containment: Limiting the scope and impact of the breach.
-
Investigation: Identifying the cause and the affected systems.
-
Eradication: removing the threat from the network.
-
Recovery: Restoring systems to normal operation as quickly as possible.
Having a structured incident response plan helps organizations respond swiftly, mitigating the damage caused by cyberattacks.
Data Protection and Encryption: Securing Sensitive Information
Data protection is one of the core principles in cybersecurity. Protecting sensitive data from theft, loss, or unauthorized access is crucial for maintaining trust and compliance with regulatory requirements. Encryption plays a key role in ensuring data privacy.
The key elements of data protection include:
-
Data encryption: Encrypting both data at rest (stored data) and data in transit (data being transmitted) to prevent unauthorized access.
-
Data backups: Regularly backing up data to prevent loss in case of an attack or hardware failure.
-
Access control: Limiting access to sensitive data based on roles and permissions.
Encrypting data ensures that even if a breach occurs, the stolen data remains unreadable and inaccessible to attackers, reducing the potential fallout.
Adapting to the Evolving Threat Environment
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, and so should your cybersecurity framework. Continuous assessment and improvement are essential to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Continuous improvement involves:
-
Regular vulnerability assessments: testing systems for potential weaknesses through tools like vulnerability scanners and penetration testing.
-
Employee training: Regular security training ensures employees stay informed about the latest threats and security best practices.
-
Staying updated: Implementing the latest security patches and updates to address new vulnerabilities.
By continually improving the cybersecurity framework, organizations can adapt to new risks and ensure their defenses remain strong over time.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires constant adaptation as threats evolve. By understanding and implementing key components like risk management, governance policies, IAM systems, security monitoring, and data protection, businesses can reduce their exposure to cyber risks. Cybersecurity is not just an IT issue but a shared responsibility across all levels. Staying vigilant and adopting a comprehensive framework helps organizations protect their data and assets and ensure business continuity in an increasingly digital world
























