Why Multi-Factor Authentication Is Essential for Security
Learn why Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is crucial for enhancing security, reducing data breaches, and protecting sensitive information from cyber threats.

As an application security expert, I’ve experienced how multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens security. By combining passwords, devices (like smartphones or tokens), and biometrics (fingerprints or facial recognition), MFA ensures that unauthorized access is significantly reduced, even if credentials are compromised.
What is multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication, or MFA, is a security protocol that requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a system, application, or network. This approach enhances security by making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have a user’s password.
Traditional authentication relies on a single factor, usually a password, which can be easily compromised. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) enhances security by adding extra layers, such as a smartphone or biometric data like fingerprints or facial recognition, reducing the risk of breaches.
MFA in Application Security & IAM
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) falls under Application Security and Identity and Access Management (IAM) within the broader field of cybersecurity.
-
Application Security: MFA is often implemented within applications to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data and functionality. It adds an extra layer of security to the authentication process, helping to protect applications from unauthorized access or breaches.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM): MFA is a crucial part of IAM frameworks, which focus on managing users' identities and controlling their access to systems, networks, and applications.
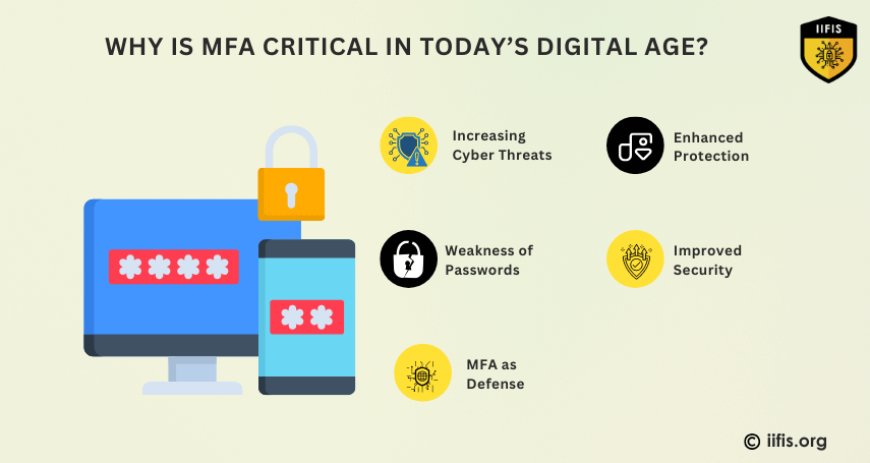
Why is MFA Critical in Today’s Digital Age?
-
Increasing Cyber Threats: Data breaches and cyberattacks are becoming more common due to hackers using tools like weak passwords, phishing, or stolen data.
-
Weakness of Passwords: Relying only on passwords is no longer sufficient to secure accounts against advanced cybercriminals.
-
MFA as Defense: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds extra layers of security, making it harder for hackers to access accounts.
-
Enhanced Protection: Even if a password is stolen, attackers need to bypass additional authentication factors (e.g., smartphone, biometric data).
-
Improved Security: MFA significantly strengthens security by requiring multiple forms of verification, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
How MFA Enhances Security Across Multiple Platforms
MFA can be implemented across various platforms, including websites, mobile applications, and enterprise systems, ensuring consistent and robust protection. Whether you're logging into your email, accessing a cloud-based application, or using an enterprise network,multi-factor authentication ensures that your data remains secure across all digital touchpoints.
Many online services offer MFA with a password plus a one-time code sent via SMS or an app. Some also use biometrics, like fingerprints or facial recognition. MFA's broad compatibility allows users to access advanced security without needing specialized equipment or complex setups.
The Role of MFA in Preventing Data Breaches
Data Breaches:
-
Over 80% of data breaches involve weak or stolen credentials (2023 Verizon Data Breach Report).
-
This highlights the vulnerability of systems that depend solely on passwords for authentication.
MFA as Protection:
-
MFA requires more than just a password, adding extra layers of security.
-
Even with stolen credentials, an attacker would still need access to the second factor (e.g., a device or biometric data).
Crucial for Security:
-
MFA significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access.
-
Its implementation is essential to prevent data breaches and safeguard sensitive information from cybercriminals.
User Experience vs. Security: Finding the Balance
-
User Experience: MFA may initially seem disruptive, but modern solutions are designed to minimize frustration and enhance security.
-
Mobile Authentication: Apps like Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator provide time-sensitive codes for quick authentication.
-
Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint scanning and facial recognition enable fast, secure, one-touch or one-glance access.
-
Future of MFA: As technology advances, MFA will become more user-friendly while maintaining strong security.
The Future of MFA: Adapting to Emerging Threats
-
Evolving Threats: As cyber threats continue to evolve, security protocols like MFA must constantly adapt to keep up with attackers' new tactics.
-
Behavioral Biometrics: Future MFA solutions could incorporate behavioral biometrics, which analyze patterns in user behavior (e.g., typing speed, mouse movements) to detect anomalies and identify potential threats.
-
AI and ML Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into MFA will allow systems to identify patterns in real-time, dynamically adapting authentication processes to better protect against evolving threats.
-
IoT and MFA: As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices continues to grow, MFA may expand to include a wider range of devices, ensuring that security remains robust across a more interconnected world. This ensures seamless protection in everyday connected devices.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is vital for securing digital assets. Pursuing an Application Security certification enhances your ability to implement MFA and other security measures, equipping you with the skills needed to protect systems and stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
























