Exploring the Basics of Information Security Foundations
Delve into the fundamentals of information security to safeguard data, mitigate risks, and ensure digital resilience.

Understanding the fundamentals of information security is important for people as well as companies in the current digital environment. Data protection, often known as cybersecurity or information security, is the process of avoiding illegal access, use, or modification.
Conformity to rules and laws is an important part of information security. To protect important data and keep out of problems with the law, organizations are frequently compelled to follow particular rules and structures, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) or the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Three fundamental principles are involved in information security.
-
Confidentiality Ensuring: Confidentiality means that confidential data is only accessed by official staff or systems. Security protocols, access controls, and encryption are some of the tools used to achieve this.
-
Integrity ensures: Information accuracy, completeness, and integrity are verified. Technologies like digital signatures, checksums, and data validation help in the identification and avoidance of unwanted data modifications.
-
Availability ensures: information is sure to be available and useful when needed. This includes security versus system and network problems, like redundancy, backups, and disaster recovery plans.
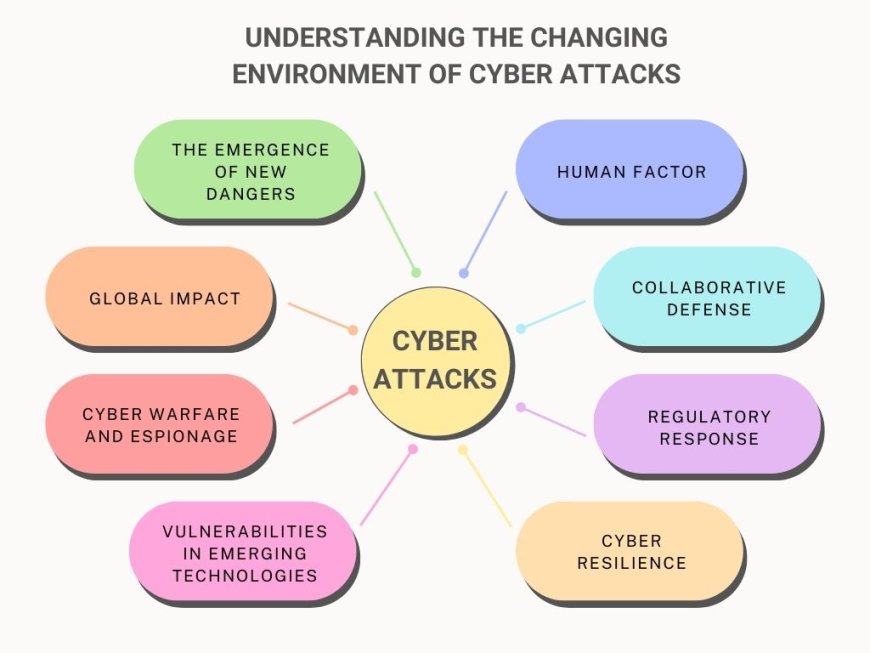
Understanding the Changing Environment of Cyber Attacks
-
The emergence of New Dangers: New dangers, including supply chain leaks and attacks driven by machine learning, are becoming increasingly important in addition to more popular ones, such as malware and phishing.
-
Global Impact: Cyber dangers affect people, companies, and governments all across the world, with no issue where they are located. Because the internet is so linked, an attack on one organization can have an important effect on many others.
-
Cyber Warfare and Espionage: There are serious dangers to national security from cyberattacks organized by states that try to damage important systems, steal confidential data, or perform espionage.
-
Vulnerabilities in Emerging Technologies: While modern technologies such as quantum computers, AI, and the Internet provide enormous advantages, they also present new security risks. To fully utilize these technologies, it is important to understand and address these risks.
-
Human Factor: Despite advances in technology, safety risks are still greatly impacted by human mistakes. Reducing risks demands teaching people about security standards and creating an environment of cybersecurity awareness.
-
Collaborative Defense: To effectively battle cybercrime, organizations including government agencies, private sector companies, and cybersecurity experts must work closely given the complexity and size of cyber dangers.
-
Regulatory Response: Governments everywhere are passing laws to improve cybersecurity and make companies responsible for data protection. To minimize criminal and financial risks, following the rules of legislation like the Consumer Credit Protection Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is important.
-
Cyber Resilience: Developing cyber security involves not just stopping attacks but also successfully expecting and handling unanticipated events. Cyber resilience measures involve making investments in cybersecurity training, developing emergency response plans, and performing regular risk assessments
Insider Dangers and Their Impacts
Insider dangers are when people who work for a company use their access to expose or do damage to confidential data. These dangers may result from inadvertent mistakes, carelessness, dark actions, or collaboration with other people.
Risks from insiders can have serious effects, such as financial losses, damage to one's good name, legal costs, and breaks to business operations. Insiders' knowledge of security mechanisms and legitimate access make detection and response difficult.
Organizations need to deploy insider threat detection technology, track user activity, regularly train employees, and put strong security measures in place to reduce insider threats. By taking preventative action, insider threats are less likely to affect company security and are protected.
What Are the Fundamentals of Information Security?
1. Confidentiality: Making sure that only approved people or organizations have access to private data. To protect data from illegal disclosure, this involves setting access controls, encryption, and data classification into action.
2. Integrity: Providing that data is dependable, accurate, and consistent over the course of its existence. Improper data changes can be identified and avoided with the use of technologies like digital signatures, verification, and data inspection.
3. Availability: Making sure that resources and information are available to those with permission when they're needed. To lessen the effects of system failures, natural disasters, or intentional attacks, redundancy, backups, and disaster recovery strategies must be implemented in practice.
4. Authentication: verifying the identity of people and companies getting access to data or systems. Passwords, fingerprints, and multiple-factor verification are examples of authentication techniques that help make sure only people with proper permission can access private information or services.
5. Authorization: Assigning users the proper rights and permissions in keeping with their jobs and responsibilities. Based on the least access principle, permission rules limit access to sensitive information and define what actions users are allowed to perform.
6. Auditability: Keeping track of user and system activity to support forensic investigation, responsibility, and provenance. To detect security problems, track changes, and look into illegitimate actions, logs, monitoring, and audit trails are useful.
7. Security Education and Training: To promote a culture of security, and raise knowledge of security issues among stakeholders, contractors, and workers. Topics include incident response protocols, phishing awareness, and safe computer actions which are covered in training courses.
8. Risk management: locating, evaluating, and managing risks to systems and information assets. Conducting risk assessments, setting controls in location, and continually reviewing security measures to adjust to changing threats and vulnerabilities are all part of risk management.
Organizations may successfully protect their information assets and reduce cybersecurity risks by following these essential principles and placing together the necessary security measures.
Information security principles offer a strong foundation for protecting confidential information and minimizing cybersecurity threats. Organizations may successfully protect their information assets by placing a high priority on risk management, security education, authorization, verification, scrutiny confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Furthermore, keeping security integrity requires tackling insider threats. Through the implementation of insider threat detection technology, user activity monitoring, and continuous security training, organizations can lower the risk associated with insiders and protect against any security breaches. Organizations must follow these guidelines and put in place the necessary security measures to have a solid level of security in the contemporary digital environment.
























