Advanced Network Security Certification for Career Growth
Boost your career with an advanced network security certification. Gain expertise in protecting networks, mitigating risks, and advancing in the cybersecurity field.

As an experienced network security professional, I’ve seen how quickly the cybersecurity landscape evolves. Advanced network security certifications have been essential for my career growth, helping me stay ahead of new threats and technologies. They’ve not only enhanced my technical skills in areas like risk management and encryption but also positioned me as a trusted leader in the field. These certifications have opened doors to leadership roles and kept me sharp by pushing me to stay updated on the latest trends. For anyone in the field, pursuing advanced certifications is a great way to further your expertise and advance your career.
What is network security?
Network security refers to the practices, technologies, and policies designed to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of a network and its data. This protection extends to both the physical network infrastructure and the devices that access the network, such as routers, switches, and servers. The ultimate goal of network security is to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, or damage to these systems while ensuring that legitimate users can access the network and its resources without disruption.
The importance of network security cannot be overstated, particularly as organizations continue to rely heavily on digital networks to run their operations. With the rise of cloud computing, mobile devices, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the potential attack surfaces have increased, requiring sophisticated security measures to keep hackers at bay.
Why is network security needed?
The need for robust network security is driven by several factors:
-
Increasing Cyber Threats: Hackers, cybercriminal organizations, and even state-sponsored groups are constantly developing new techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in networks. These threats range from malware and phishing to more sophisticated attacks like distributed denial of service (DDoS) and ransomware. Without strong security, networks are vulnerable to breaches that can have catastrophic financial, legal, and reputational consequences.
-
Data Protection and Privacy: With the advent of regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), companies are legally obligated to protect the personal and sensitive data of their customers. A data breach not only damages a company’s reputation but can also result in significant financial penalties.
-
Remote Work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to remote work, which has persisted in many industries. This transition has expanded the potential attack surface, as employees are accessing company networks from various locations and devices. Ensuring secure remote access has become a top priority for businesses of all sizes.
-
Business Continuity: Cyber attacks like ransomware can shut down critical business operations for extended periods, leading to costly downtime. Strong network security measures ensure that business continuity is maintained and that recovery processes are in place in case of an attack.
-
Intellectual Property and Competitive Advantage: For many companies, their intellectual property is their most valuable asset. Protecting proprietary data and other business-critical information from theft is essential for maintaining a competitive advantage in the market.
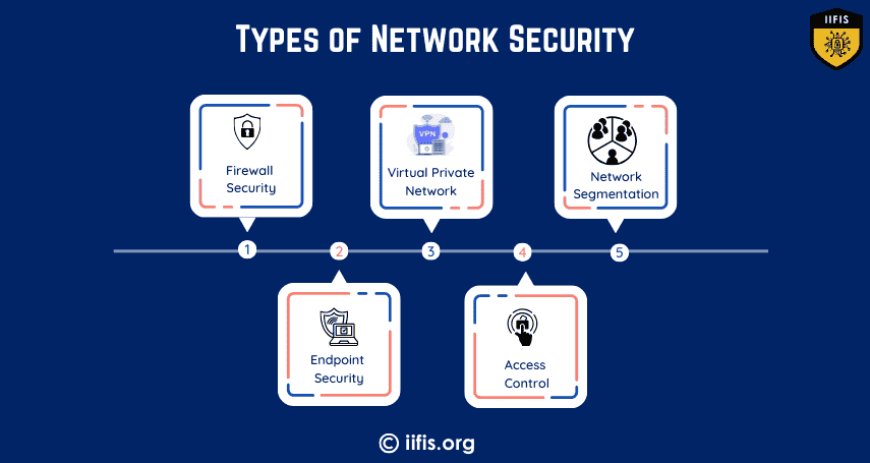
What Are the Types of Network Security?
Network security encompasses a variety of tools, technologies, and practices to protect a network. These are broadly categorized into the following types:
-
Firewall Security: Firewalls are used to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. They act as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, like the Internet.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IDS and IPS are designed to detect and prevent unauthorized access or attacks on a network. IDS identifies suspicious activity, while IPS takes proactive steps to block potential threats.
-
Virtual Private Network (VPN): VPNs encrypt internet traffic, allowing users to securely access a network remotely. This is especially important for remote workers or those accessing the network from public Wi-Fi networks.
-
Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: These tools scan for malicious software that may infiltrate a network, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans. Keeping these programs up to date is crucial for protecting against evolving threats.
-
Access Control: Access control mechanisms determine who can access which resources on a network. This can be implemented through authentication methods like passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication (MFA), ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive systems.
-
Encryption: Encrypting data both in transit and at rest ensures that even if data is intercepted by an unauthorized party, it will be unreadable without the decryption key.
-
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): SIEM tools collect and analyze security-related data from across the network, helping to detect anomalies and threats in real time.
-
Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller, isolated sections can limit the impact of a breach, restricting attackers’ movement within the network and reducing the overall attack surface.
-
Endpoint Security: Securing devices that connect to the network—such as computers, smartphones, and IoT devices—ensures that these endpoints do not become points of vulnerability for the entire system.
Which Are the Best Network Security Certifications?
Several important certifications in cybersecurity can help you advance your career:
CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional) is a well-known certification for those aiming for leadership roles in cybersecurity. It covers topics like network security, access control, and risk management, making it ideal for experienced professionals looking to move into senior positions.
CISM (Certified Information Security Manager) focuses on managing information security programs. It’s great for those who want to take on leadership roles and oversee security teams, with an emphasis on governance and risk management.
For those interested in network security specifically, the Certified Network Security Professional (CNSP) is a good option. This certification focuses on securing network infrastructures and includes topics like firewalls, VPNs, and network defense.
As many businesses move to cloud services, the Certified Cloud Security Expert (CCSE) is becoming increasingly valuable. It teaches how to secure cloud platforms and data, which is essential for anyone working in or moving toward cloud security roles.
Lastly, the AI Cyber Security Associate certification focuses on using artificial intelligence to detect and respond to cyber threats. With the rise of AI in cybersecurity, this certification is perfect for those interested in combining both fields.
Each of these certifications focuses on different areas of cybersecurity and can help you gain specialized knowledge and advance in the field.
A Great Path to Network Security Certification
For anyone looking to pursue a career in network security, following a clear path of certification can be incredibly beneficial. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you on your way:
-
Start with the Basics: If you’re new to the field, begin with foundational certifications like CompTIA Security+ or the Cisco CCNA. These certifications provide a solid understanding of networking principles and basic security concepts.
-
Build Experience: Practical experience is invaluable. Look for internships, entry-level jobs, or volunteer opportunities to gain hands-on experience with network security tools, threat detection, and network monitoring.
-
Advance Your Knowledge: Once you have some experience, consider more specialized certifications like CEH or CompTIA Network+ to dive deeper into specific areas of network security. You can also pursue CISSP if you’re interested in management or leadership roles.
-
Stay Current: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. It’s crucial to keep up with the latest trends and technologies in network security. Participate in professional development opportunities, attend conferences, and regularly refresh your certifications.
-
Seek Mentorship: Connecting with experienced professionals in the field can provide valuable insights and career guidance. Mentors can help you navigate complex security challenges and offer advice on advancing your career.
Advanced network security certifications are key to staying ahead in a fast-changing cybersecurity environment. They enhance your expertise, open doors to leadership roles, and ensure you’re prepared to tackle new challenges. By continually advancing your skills, you can secure a successful, long-term career in network security.























