Applications of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity applications include data protection, network security, threat detection, identity management, and secure communication, ensuring privacy and safety.

Cybersecurity has become an essential part of our lives, and from my experience in the field, I've seen how quickly the environment has changed. In the beginning, securing devices seemed straightforward—basic firewalls and antivirus programs were enough. However, as cyber threats became more advanced, the need for stronger protections like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and AI-driven threat detection grew significantly. Over time, security measures have evolved to address new challenges, from protecting personal data to securing entire networks and critical infrastructures. It’s been a fascinating journey, and I’ve learned that continuous learning and staying updated with new technologies are essential to staying ahead in this field.
What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital threats, such as unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. It involves implementing a variety of tools, policies, and strategies to safeguard sensitive information, ensure privacy, and maintain the integrity of critical systems.
From protecting personal emails to securing financial transactions and corporate networks, cybersecurity plays an integral role in securing our digital world. It has evolved significantly over the years as cyber threats become more sophisticated and pervasive.
How Cybersecurity Works: Key Applications
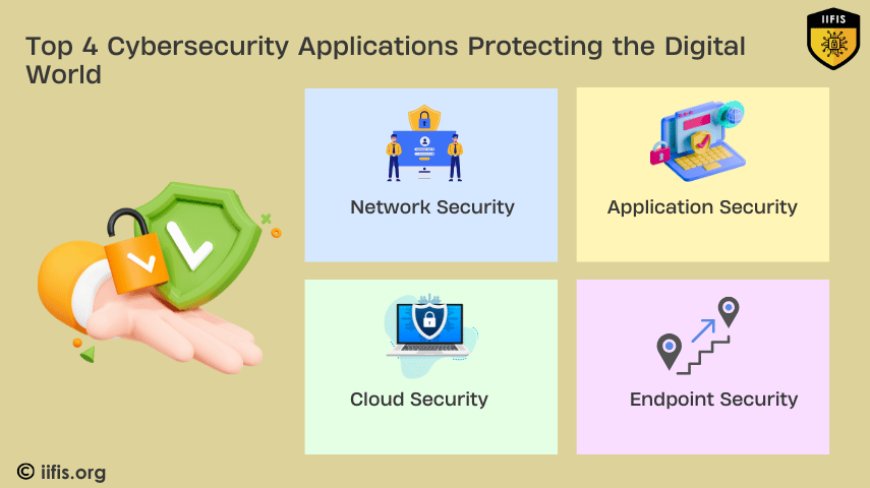
Cybersecurity applications encompass a broad range of technologies and practices designed to protect systems and data. Below are some of the key areas of cybersecurity and how they work:
Network Security
Network security focuses on protecting the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of data as it travels across networks. This includes securing devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls and implementing intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS). VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are used to encrypt communications over public networks, ensuring secure data transfer.
Application Security
Application security is about ensuring software is free from vulnerabilities that can be exploited by attackers. This includes secure coding practices, code reviews, and the use of Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) to protect against common threats like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
Cloud Security
Cloud security protects data stored in cloud environments. This includes encryption of both data at rest and in transit, as well as implementing strong access control mechanisms like multi-factor authentication (MFA). Tools like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) help organizations monitor cloud configurations and prevent misconfigurations that can lead to security breaches.
Endpoint Security
As the use of personal devices in the workplace increases, endpoint security ensures that laptops, smartphones, and tablets are secure. This involves using antivirus software, firewalls, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools to monitor and respond to threats on these devices.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that only authorized individuals can access specific resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, while Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to authenticate once and access multiple services without repeatedly logging in.
Data Security
Data security protects sensitive data from unauthorized access or theft. Encryption is used to secure data both during transmission and while stored. Additionally, Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools are implemented to prevent data leakage from internal or external sources.
Incident Response and Threat Management
An incident response plan outlines strategies for identifying, responding to, and recovering from security incidents. Threat intelligence helps anticipate and prevent potential attacks, while forensics tools are used to investigate and understand the source of an attack.
Skills Required for a Career in Cybersecurity
A career in cybersecurity requires both technical and soft skills. Here's a breakdown of the key competencies needed to succeed in this field:
Technical Skills
-
Networking Knowledge: Understanding protocols such as TCP/IP, DNS, and HTTP is essential for protecting networks.
-
Cryptography: The ability to implement encryption algorithms and secure communications is crucial.
-
Programming & Scripting: Familiarity with programming languages (Python, C++, Java) helps automate tasks and detect vulnerabilities in software.
-
Risk Management: Assessing and mitigating security risks through vulnerability assessments and security controls.
-
Threat Detection & Analysis: Using threat intelligence and anomaly detection to identify potential threats in real time.
Soft Skills
-
Problem-Solving: Cybersecurity professionals must be adept at solving complex problems under pressure.
-
Attention to Detail: Detecting vulnerabilities or unusual behavior requires careful attention.
-
Communication Skills: Explaining security issues and risks to non-technical stakeholders is crucial.
Prerequisites and Requirements for Cybersecurity
While a formal degree in computer science or information security is helpful, it's not always necessary. Here are some steps to help you get started in cybersecurity:
Educational Background
-
Bachelor’s Degree: A degree in IT, computer science, or related fields is often preferred.
-
Certifications: Certifications are vital for building knowledge and credibility. Some of the most recognized certifications in cybersecurity include:
-
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
-
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
-
IIFIS Cybersecurity Certifications: These certifications focus on securing financial systems, data privacy, and mitigating cyber threats in the digital economy.
Hands-On Experience
-
Internships: Gaining real-world experience through internships is an excellent way to build your skills.
-
Virtual Labs & Tools: Set up your virtual environment using platforms like Kali Linux or Wireshark to practice penetration testing and security configurations.
-
Capture the Flag (CTF) Challenges: Participating in CTF challenges helps sharpen your ethical hacking skills and learn about vulnerabilities.
People Also Ask: Common Cybersecurity Interview Questions
If you're preparing for a cybersecurity interview, here are some common questions that you may encounter. These questions cover various aspects of cybersecurity, from technical skills to real-world problem-solving scenarios:
1. What is the difference between a virus, worm, and Trojan?
-
Answer: A virus attaches itself to a legitimate program and spreads when the program is executed. A worm is a self-replicating program that spreads through networks. A Trojan is a malware disguised as legitimate file or software.
2. What is multi-factor authentication (MFA), and why is it important?
-
Answer: MFA requires users to provide two or more verification factors—something they know (password), something they have (a smartphone), or something they are (fingerprint). It enhances security by adding additional layers of protection beyond just a password.
3. What is a firewall, and how does it work?
-
Answer: A firewall monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. It acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks.
4. Can you explain the concept of penetration testing and its role in cybersecurity?
-
Answer: Penetration testing is the practice of testing a system or network for vulnerabilities by simulating an attack. The goal is to identify weaknesses before malicious hackers can exploit them.
5. What are the different types of encryption, and how do they work?
-
Answer: The two primary types of encryption are symmetric encryption (where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption) and asymmetric encryption (which uses a pair of keys: public and private). Each serves different purposes in securing data.
6. What are some of the most common cybersecurity threats organizations face today?
-
Answer: Some common threats include phishing attacks, ransomware, SQL injection, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, and insider threats.
7. How would you respond to a data breach incident?
-
Answer: A well-prepared incident response plan is critical. The first step is to contain the breach, assess the damage, and notify the necessary parties. Then, perform a forensic investigation to determine the cause and impact, followed by recovery steps to restore affected systems.
8. What are Security Operations Centers (SOCs), and why are they important?
-
Answer: A Security Operations Center (SOC) is a centralized unit that monitors, detects, and responds to security threats in real time. SOCs are essential for identifying threats quickly and minimizing damage from cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity is an exciting and growing evolving field. Whether you're looking to protect personal information or secure critical business systems, the demand for skilled cybersecurity professionals is at an all-time high. By acquiring the right knowledge, gaining hands-on experience, and earning the necessary certifications, you can embark on a rewarding career in cybersecurity.























