Certified Cyber Security Manager Securing Your Network
Learn how a Certified Cyber Security Manager ensures your network is secure, protecting sensitive data and keeping your business safe from evolving cyber threats.

As a cyber security expert, I can confidently say that with the increasing reliance on technology, securing your network is no longer optional; it's critical. Cyber threats, ranging from data breaches to sophisticated ransomware attacks, are becoming more frequent and destructive. Organizations must adopt a proactive approach to safeguard their infrastructure. This is where a Certified Cyber Security Manager comes in. These professionals bring the necessary expertise and skills to effectively protect networks, ensuring sensitive data remains secure and business operations continue without disruption. Their role is pivotal in staying ahead of evolving cyber threats.
The Growing Need for Cyber Security Professionals
The digital age has brought many benefits, but it has also made cyber threats more complex. As technology advances, hackers become more skilled, and organizations face more frequent and serious security breaches. In this environment, the role of a Certified Cyber Security Manager is more vital than ever. These professionals are experts in protecting networks and systems from both internal and external threats, ensuring that critical data remains secure.
Cybersecurity experts are tasked with developing and implementing security policies, conducting risk assessments, and responding to incidents. Their job is to ensure that the network infrastructure is resilient and that potential vulnerabilities are identified and addressed before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
Key Responsibilities of a Certified Cyber Security Manager
A Certified Cyber Security Manager holds a wide range of responsibilities. Their role includes, but is not limited to:
-
Risk Management: Assessing and identifying potential risks to the organization’s network and implementing strategies to mitigate those risks.
-
Security Policy Development: Creating security protocols that align with industry standards and organizational goals.
-
Incident Response: Leading efforts to detect, respond to, and recover from security breaches or cyber-attacks.
-
Network Monitoring: Continuously monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and implementing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS).
-
Compliance Management: Ensuring that the organization adheres to necessary legal, regulatory, and industry standards, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
-
Employee Training: Educate staff about best practices for maintaining security, including safe internet browsing, email hygiene, and handling sensitive data.
These professionals must be proactive, keeping up with new threats and implementing the latest security measures to keep organizations safe.
Securing Your Network: Why It Matters
The core of every business's digital infrastructure is its network. Whether it’s an internal office network or a company’s public-facing website, security must be a top priority. A Certified Cyber Security Manager ensures that the network infrastructure remains secure and reliable. Here’s why network security matters:
-
Protection from Cyber Attacks: Networks are prime targets for cybercriminals seeking unauthorized access to sensitive data. Without strong security measures, organizations can become vulnerable to attacks like data breaches, ransomware, and denial-of-service attacks.
-
Preserving business continuity: A compromised network can lead to downtime, lost revenue, and a damaged reputation. A Certified Cyber Security Manager ensures that businesses continue to operate smoothly even in the face of potential threats.
-
Safeguarding sensitive data: Networks often store valuable information, such as customer data, intellectual property, and financial records. Protecting this data is crucial for maintaining trust with clients and complying with data protection regulations.
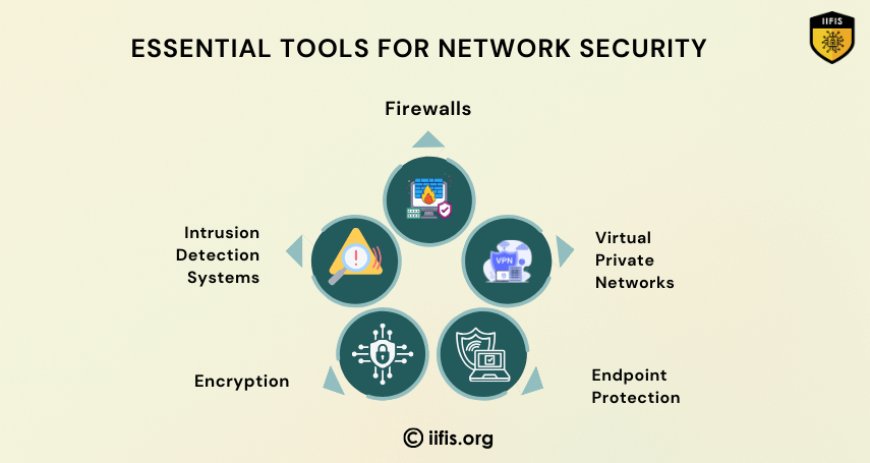
Essential Tools for Network Security
Securing a network requires the use of various tools and technologies. A Certified Cyber Security Manager is proficient in using these tools to create a defense strategy for the organization. Here are some essential tools they may use:
-
Firewalls: These are the first line of defense, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can automatically take action to block potential threats.
-
Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data ensures that even if it’s intercepted, it cannot be read without the decryption key.
-
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs provide secure communication channels for remote employees and protect data from eavesdropping over public networks.
-
Endpoint Protection: Security software on devices connected to the network (laptops, smartphones, etc.) ensures that each device is secure and does not serve as an entry point for cybercriminals.
By using these tools and maintaining a comprehensive security framework, a Certified Cyber Security Manager can create a resilient defense against evolving cyber threats.
How Certification Elevates a Cyber Security Career
While practical experience in the field of cyber security is essential, obtaining certification significantly boosts a professional’s credibility and career opportunities. The role of a Certified Cyber Security Manager requires not only technical expertise but also an understanding of broader business strategies. Certification demonstrates that the individual has mastered the necessary skills to protect an organization’s network and systems.
Certification programs typically include both theoretical knowledge and hands-on experience, ensuring that professionals are prepared for the challenges they will face in real-world environments. For those seeking career advancement, obtaining a recognized certification, such as from the International Institute of Information Security (IIFIS), can open doors to higher-paying positions and more responsibilities.
Best Practices for Network Security
A Certified Cyber Security Manager relies on industry best practices to ensure that an organization’s network remains secure. Here are some best practices they typically implement:
-
Regular Software Updates: Ensuring that all software, including operating systems and applications, is updated regularly to patch security vulnerabilities.
-
Strong Authentication Methods: Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance access control and prevent unauthorized entry.
-
Least Privilege Principle: Granting users only the minimum access necessary to perform their tasks, reducing the risk of internal threats.
-
Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address any weaknesses in the network security infrastructure.
-
User Awareness: Educate employees about phishing attacks, password management, and other cyber threats they may encounter.
By continuing to follow these best practices, a Certified Cyber Security Manager helps build a culture of security within the organization, minimizing risks and ensuring compliance.
The Future of Cyber Security Management
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the demand for skilled Certified Cyber Security Managers will only increase. Professionals in this field will need to adapt to emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and blockchain to stay ahead of cybercriminals.
The future of cyber security will also involve closer collaboration between IT departments, legal teams, and upper management to create more integrated and comprehensive security strategies. Organizations will continue to rely on certified professionals to safeguard their networks, data, and infrastructure, making this career path highly rewarding.
























