Understanding AI Security Certification
Explore the significance of AI security certification, ensuring robust protection against emerging threats. Learn more about safeguarding AI systems effectively.

Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, which promise efficiency and innovation, are growing as fundamental instruments in the fastly evolving field of modern technology. But in the digital world, trust and integrity must be preserved above all else, which means making sure these systems are secure. Taking up the challenges of AI security certification as the CTO of a top IT company is no easy feat. Significant issues arise from a shortage of common methods and the active nature of threat environments. Despite these challenges, becoming certified by reliable authorities is important for proving your dedication to data security and reducing risks, which will increase confidence and trust in AI deployments.
Proactive risk management techniques are critical for effectively handling the complexities of AI security certification. This entails working with colleagues in the sector, putting strong security measures into place, and keeping up with new dangers. Through proactive measures, organizations can protect sensitive data and maintain stakeholder trust while promoting innovation and digital transformation in the current day through the integrity and safety of their AI systems.
What is AI Security Certification
-
AI security certification functions as a thorough assessment procedure that covers a range of design, implementation, and operation-related topics for AI systems.
-
It entails evaluating the AI system's handling and security of sensitive data and making sure it complies with data protection laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
-
The certification process looks at the AI system's ability to fight online dangers, including any holes or flaws that could be used by bad actors.
-
By confirming the integrity of the AI algorithms, it reduces the possibility of prejudice or discrimination while guaranteeing dependable and accurate outcomes.
-
Additionally, certification assesses how transparent and explicable the AI system's decision-making procedures are, allowing users to understand how and why particular results are produced.
-
It also evaluates the resilience of the AI system's operational protocols and infrastructure, including incident response and disaster recovery plans.
-
Organizations must put in place procedures for continuing risk assessment and mitigation to benefit from AI security certification, which promotes continual monitoring and development.
-
It promotes industry cooperation and knowledge exchange, which helps to create industry standards and best practices for AI security.
-
In the end, AI security certification increases the confidence and trust that stakeholders and users have in AI systems, which promotes their acceptance and use across a range of fields.
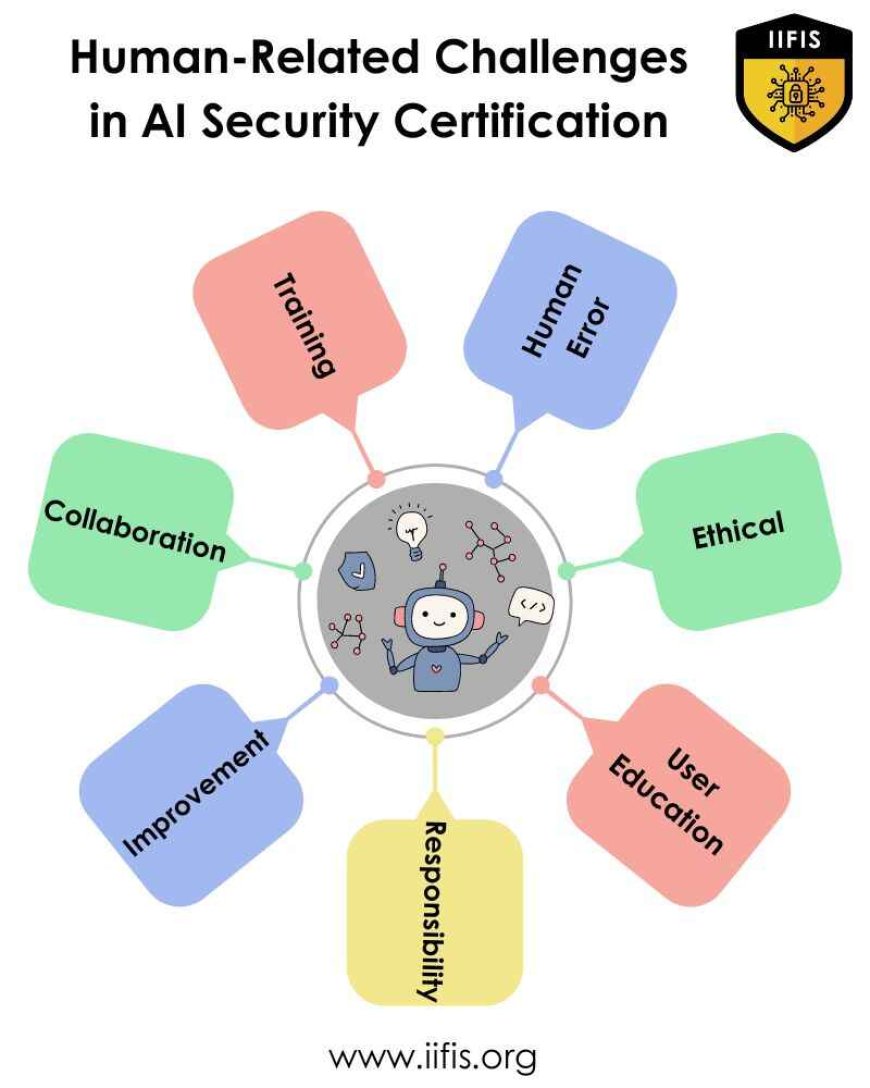
Addressing Human-Related Challenges in AI Security Certification
-
Training and Awareness:
Making sure that everyone involved in creating and implementing AI systems is aware of the significance of security is one important factor. This entails educating people about potential dangers and risks as well as offering training on best practices for safeguarding AI systems.
-
Human Error Mitigation:
Because humans are prone to error, the security of AI systems may unintentionally be damaged. Human error as a cause of security breaches can be minimized by putting procedures in place like double-checking setups and doing extensive testing.
-
Ethical Considerations:
The ethical considerations surrounding AI security, including data collection, use, and protection, can be influenced by human judgments. AI security certification procedures that incorporate ethical frameworks and rules can assist in guaranteeing that human decision-making adheres to moral standards.
-
User Education:
Security issues also affect AI system end users. Clear guidelines and directions on the safe usage of AI systems can help avoid common dangers like unintentionally exposing sensitive information or falling prey to phishing attacks.
-
Accountability and Responsibility:
Addressing human-related issues in AI security requires defining distinct lines of accountability and duty. This entails outlining the roles and duties of those working on creating, implementing, and maintaining AI systems as well as holding them responsible for any potential security breaches.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
To keep ahead of new dangers, humans must constantly review and improve AI security measures. This involves keeping up with newly identified security dangers, routinely upgrading security procedures, and applying lessons learned from previous security incidents to avert such problems in the future.
-
Collaboration and Communication:
To overcome human-related difficulties in AI security certification, developers, security experts, policymakers, and end users must effectively collaborate and communicate with each other. We can all work together to increase the security of AI systems by exchanging information and insights.
How does AI security certification differ from traditional cybersecurity practices?
-
Focus on AI-specific Risks:
The special dangers and weaknesses related to artificial intelligence systems are addressed by AI security certification. This covers issues that typical cybersecurity techniques might not fully address, like data tampering, model bias, and adversarial attacks.
-
Specialized Expertise:
Certification in AI security necessitates specific knowledge of cybersecurity and AI technologies. It entails comprehending not only the complexities of AI algorithms and their possible security implications but also more conventional security methods like security and access control.
-
Evaluation of AI Models:
In contrast with standard cybersecurity procedures, certification for AI security entails assessing the security of AI models independently of the systems and infrastructure on which they are installed. This entails evaluating how resilient AI models are to hostile attacks and making sure they don't display prejudice or discrimination.
-
Transparency and Explainability:
More focus is placed on explainability and openness in AI security certification. It necessitates making sure AI systems can explain their decisions and be transparent in the process of making them, which might not be as important in conventional cybersecurity procedures.
-
Regulatory Compliance:
Regulations unique to AI security are becoming increasingly important as AI is used in delicate fields like banking and healthcare. AI security certification guarantees that AI systems comply with legal criteria and uphold ethical principles meant to safeguard individuals' privacy and avoid prejudice.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation:
AI security certification acknowledges the necessity of ongoing observation and adjustment in response to changing risks and threats. Security measures need to be updated and modified frequently to handle new vulnerabilities and attack vectors because AI technologies are dynamic.
-
Interdisciplinary Approach:
An interdisciplinary strategy, comprising cooperation between cybersecurity specialists, AI researchers, ethicists, policymakers, and domain-specific professionals, is frequently necessary for AI security certification. This combination of disciplines is crucial for handling the intricate problems related to AI system security.
AI security Certification guarantees honesty and reliability in quickly developing AI technology. It assesses algorithm integrity, transparency, resilience, threat defense, and data handling. The key is to address human-related difficulties, which call for cooperation, ethical concerns, user education, error mitigation, training, and responsibility. In contrast to traditional cybersecurity, artificial intelligence (AI) certification stresses openness, guarantees regulatory compliance, demands specialized expertise, assesses AI models independently, and promotes ongoing monitoring. It also focuses on hazards unique to AI. Multidisciplinary thinking is essential. In general, certification raises people's confidence and trust, which promotes the adoption of AI across industries while preserving data integrity and moral principles.