Understanding Network Security: A Simple Guide
Learn the basics of network security, its importance, real-world data breaches, and how to protect your digital information from cyber threats
What is a Network?
In simple terms, a network is like a group of people who can talk to each other. But instead of humans, it’s computers, devices, and servers communicating over wires or wireless connections. Think of your phone connecting to Wi-Fi, or your laptop talking to a printer on the same network. That’s a computer network.
For example, when you browse the internet, your computer connects to websites via a network, which allows you to send requests and receive data in return (like loading a webpage or watching a video).
How Does a Network Work?
Networks work through protocols—rules that tell devices how to communicate. Imagine if everyone spoke the same language; that’s how protocols work. The most common one you’ve probably heard of is TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), which controls how data travels between devices on a network. Devices send small pieces of information (called packets) to each other, and those packets eventually come together to form the complete data.
An easy example: When you send a message on WhatsApp, it travels through various networks to reach the recipient. The network ensures your message gets from one phone to another.
Why Do We Need Networks?
Networks make our digital lives easier, faster, and more efficient. Here’s why:
-
Connection: We can share files, print documents, or talk to others on the same network.
-
Efficiency: Instead of each device working in isolation, they work together, sharing data and resources (like a shared printer).
-
Access to Information: The internet, which is essentially a massive network of networks, gives us access to almost endless information and services.
Advantages of Networks
-
Resource Sharing: Networks allow devices to share resources. For instance, several computers in an office can share the same printer.
-
Communication: They enable fast and easy communication—whether it’s an email, video call, or instant messaging.
-
Centralized Data: Networks let you store data on one central server, and access it from any device connected to the network.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Instead of every device having to store all the data or perform all tasks, devices can access shared resources.
What is Network Security?
Just like we lock doors to protect our homes, network security is the practice of protecting a computer network from harmful attacks, unauthorized access, and potential threats. In simple words, network security ensures that only the right people can use the network, and the data being shared on it stays safe and secure.
Why is Network Security Important?
Every time you send a message, make a transaction, or use a service online, you’re trusting the network to protect your sensitive data. Without network security, hackers could access your personal information, steal money, or damage your devices. Here are a few examples of security threats:
-
Malware: Harmful software that can damage your devices or steal data.
-
Phishing: Fake emails or websites that trick you into giving up personal information, like passwords or credit card numbers.
-
Denial of Service (DoS): Attacks that overwhelm a network to make it unavailable for legitimate users.
-
Man-in-the-middle attacks: Hackers who secretly intercept communications between two devices to steal data.
Real-Time Examples of Data Breaches
Data breaches have become a common and alarming threat in today’s digital world. These incidents show just how crucial network security is. Here are a few major examples:
-
Equifax Data Breach (2017): One of the largest and most infamous breaches, hackers gained access to the personal information (including social security numbers) of 147 million people due to a vulnerability in a web application. This breach highlighted how important it is to secure sensitive personal data.
-
Target Data Breach (2013): Hackers accessed the credit card information of 40 million customers. The breach occurred because attackers stole login credentials from a third-party vendor. This breach showed the risks involved in not securing connections to third-party services.
-
Yahoo Data Breach (2013-2014): In one of the largest breaches in history, hackers stole information from 3 billion Yahoo accounts, including email addresses, passwords, and security questions. The breach wasn’t discovered until years later, highlighting the importance of constant monitoring and swift response.
-
Facebook Data Breach (2019): This breach exposed the personal data of over 540 million Facebook users. The data was stored on an unprotected server, making it accessible to anyone with the right skills. It emphasized the need for proper data storage and privacy controls.
These breaches demonstrate the massive impact that security lapses can have on both individuals and organizations. With so much of our personal and financial data online, protecting networks is critical.
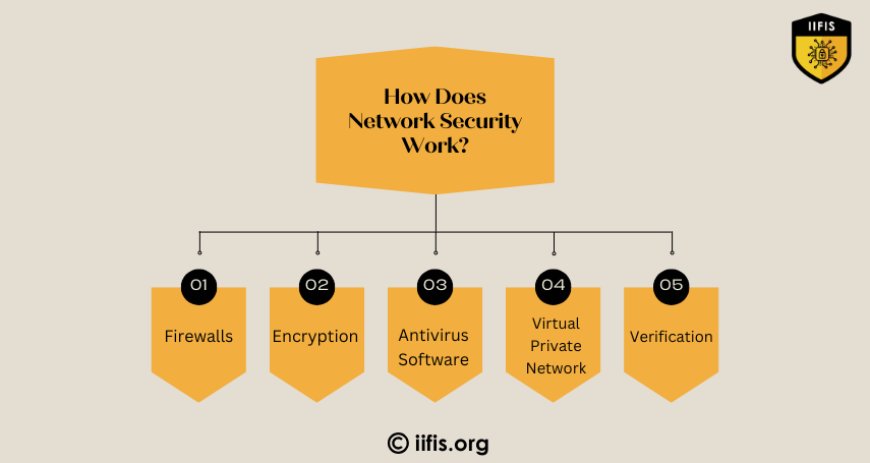
How Does Network Security Work?
Network security uses various tools and methods to keep your information safe. Here are a few common ones:
-
Firewalls: These act like a security guard for your network, blocking harmful traffic and allowing only safe data to pass.
-
Encryption: This turns your data into unreadable code so that even if hackers intercept it, they won’t be able to understand it without the decryption key.
-
Antivirus Software: These programs constantly scan for viruses or malware and block them before they can harm your devices.
-
VPN (Virtual Private Network): It creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet, hiding your online activity from hackers.
-
Authentication: To access certain parts of a network, you might need a password, fingerprint, or other identification methods to prove that you are who you say you are.
Advantages of Network Security
-
Protects Sensitive Data: Encryption and authentication methods ensure that your personal and financial data remain private.
-
Prevents Unauthorized Access: Only authorized people or devices can access certain parts of the network.
-
Maintains Trust: Users feel more comfortable interacting with networks that are secure because they know their information is protected.
-
Prevents Downtime: Effective security measures prevent attacks that could cause your network to crash or become unavailable.
Why Pursue Network Security Certifications?
As cyber threats continue to rise, network security professionals are in high demand. Pursuing certifications in network security not only boosts your credibility but also equips you with the skills needed to secure systems effectively.
Here are a few popular network security certifications to consider:
-
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): A more advanced certification, ideal for professionals looking to take their expertise to the next level. It covers a wide range of topics, including risk management and network security architecture.
-
CompTIA Security+: An entry-level certification for those just getting into network security. It covers foundational topics like threat management, cryptography, and network infrastructure.
-
Certified Network Security Professional (CNSP): This certification focuses on building practical skills for securing networks. It’s ideal for those looking to work hands-on with security infrastructure, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and VPNs.
-
Certified Cloud Security Expert (CCSE): With more organizations migrating to the cloud, this certification is essential for professionals who want to specialize in securing cloud environments. It covers cloud architecture, compliance, and security measures for cloud-based systems.
Network security is crucial to protect sensitive data and ensure the safety of our digital interactions. As we rely more on networks for everything from personal communication to business operations, it’s essential to understand the potential risks and the measures needed to defend against them. Real-world examples, like the Equifax and Target data breaches, show just how damaging poor network security can be. By using tools like firewalls, encryption, and antivirus software, network security keeps our information safe from cyber threats.
























