Fundamentals for Network Security Professionals
Discover essential fundamentals for network security professionals. Learn key concepts, strategies, and best practices to safeguard digital assets.

Professionals with expertise in network security are in high demand across a range of businesses. Companies are particularly vulnerable to cyberattacks since they mostly depend on digital networks to transmit and store important information. Particularly sensitive industries include finance, healthcare, and government; therefore, strong safety precautions must be designed and put into place by qualified specialists to protect against attacks.
Experts in network security are increasingly needed since developments like cloud computing and remote work increase the attack surface. In addition to preventing cyberattacks, these experts are important for incident response and recovery, which maintains business continuity and complies with regulations. The need for qualified network security specialists will only increase as technology develops, offering those who are passionate about safeguarding digital assets a potential career path.
The challenges faced by network security professionals
-
Ever-Evolving Cyber Threats: Network security experts frequently find it difficult to keep up with the changing cyber-attack environment. Hackers are always coming up with new methods and ways to take advantage of imperfections, so you have to be alert and flexible constantly.
-
Complexity of Modern Networks: Unexpected network complexity has resulted from the introduction of modern technologies like cloud computing, IoT, and software-defined networking. It needs specific expertise in fields like cloud and IoT security, as well as all-encompassing interoperability and seamless integration tactics, to secure these complex systems.
-
Resource Constraints: Organizations frequently find it difficult to invest in the latest security employees and technology due to limited resources and personnel. Within the constraints of their resources, experts must come up with creative and economical ways to improve network security while giving initiatives a risk-based priority list and making use of open-source software.
-
Navigating Organizational Structures: To properly deploy cybersecurity actions, network security specialists must cross difficult organizational structures and interact with a variety of departments and stakeholders. Successful communication, diplomacy, and alignment with the organization's objectives and compliance standards are necessary for success.
-
Balancing Security and Usability: Finding the right balance between usability and security is important. Experts need to create security guidelines and plans that offer a strong defense without hindering user output or causing differences with clients. To minimize user impact and simplify security processes, it is imperative to collaborate with stakeholders to build user-friendly safety systems.
Network security professionals need to manage intricate networks, maximize resources, and adjust to new dangers. Crucial elements include clear communication, objective alignment, and striking a balance between security and usability. Initiative prioritization and teamwork improve security without sacrificing output or user experience.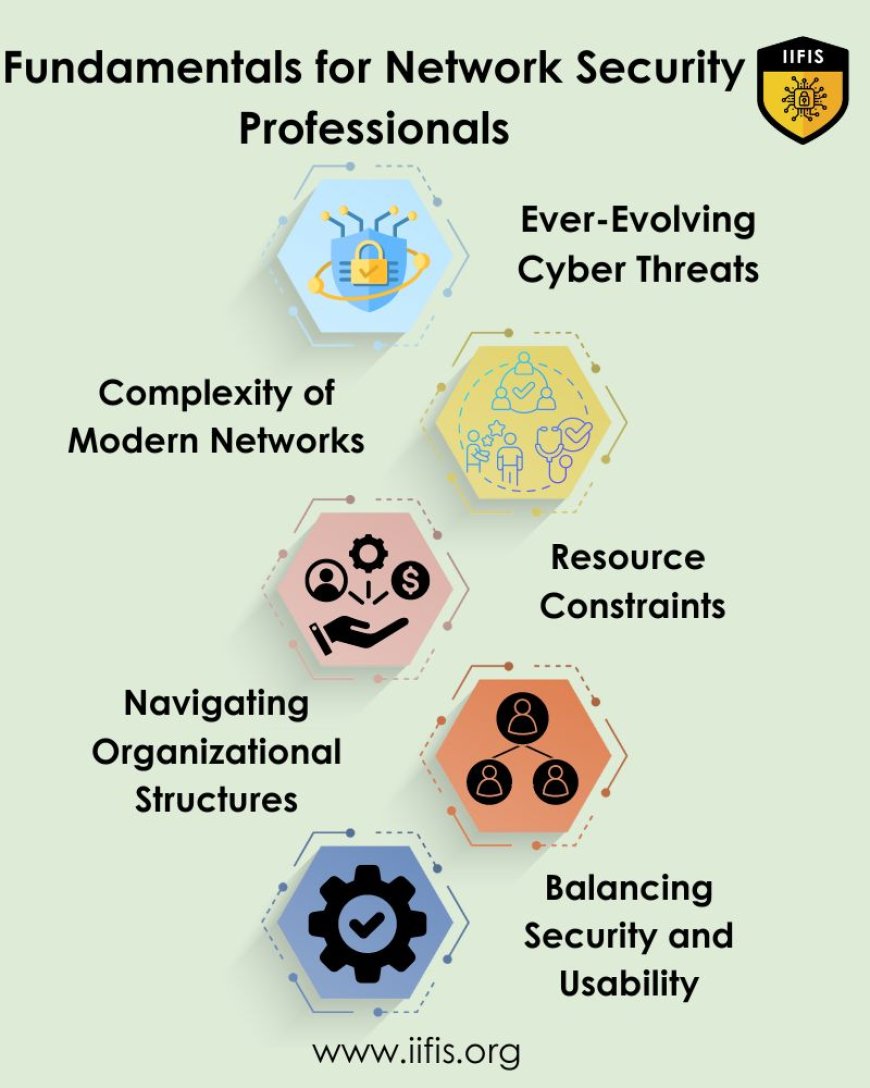
How Can Network Security Professionals Safeguard Against Evolving Cyber Threats?
Network security experts can defend against changing cyber threats by maintaining vigilance and using a multi-layered strategy. How to do it is as follows:
-
Regular Updates and Patch Management: Update all software with the most recent security patches, including operating systems and apps. By doing this, identified weaknesses that an attacker might use are closed.
-
Strong Password Policies: Implement stringent password policies for all systems and networks. To provide an additional degree of protection, promote the use of complicated passwords or passphrases and, when practical, utilize multi-factor authentication.
-
Network Segmentation: Divide networks into smaller parts to limit the effect of a possible security compromise. This lessens the extent of the attack and limits an attacker's ability to move laterally across the network.
-
Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Install firewalls to keep track of and control all network traffic, both coming in and leaving out. Use intrusion detection systems as well to identify and address any questionable activity or possible safety risks.
-
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: To find loopholes in network defenses, conduct regular attacks and security audits. This helps in proactively fixing problems before attackers take use of them.
-
Employee Training and Awareness: Instruct staff members on cybersecurity best practices and spread knowledge about typical dangers like social engineering and phishing scams. Workers ought to receive training on spotting and reporting suspicious activity.
-
Encryption: Protect sensitive data while it's in transit and at rest. This makes sure that data is unintelligible to unknown users even if it is collected.
-
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response: Use tools for ongoing tracking to quickly identify and address security problems. Create and maintain an incident response strategy to efficiently lessen the effects of security problems.
-
Vendor Risk Management: Evaluate and keep updated on the security procedures used by outside suppliers and service providers. To stop supply chain dangers, make sure they follow the necessary security guidelines.
-
Threat Intelligence Sharing: Interact in forums that share security information to keep up-to-date on new dangers and attack methods. This body of information may help in improving security against constantly changing cyber threats.
Uses of Network Security
Protecting Data:
-
Uses access controls and security to protect sensitive data against theft, illegal access, and modification.
Preventing Unauthorized Access:
-
Uses firewalls and methods for verification to prevent harmful software or unknown users from accessing networks and systems.
Ensuring Availability:
-
Understand problems such as denial-of-service assaults to ensure continuous access to network resources and services.
Maintaining Privacy:
-
Protects the privacy of data and communications by securing both in-transit and at-rest data.
Detecting and Responding to Threats:
-
Uses intrusion detection systems and security information management solutions to quickly identify and address security risks.
Complying with Regulations:
-
Supports companies in meeting legal and regulatory obligations about privacy and data protection.
Protecting Reputation:
-
Protects companies' reliability and image by averting data leaks and cyberattacks.
Supporting Business Continuity:
-
Helps with backup and recovery efforts, making sure business activities continue undisturbed.
Facilitating Secure Remote Access:
-
Permits mobile and distant workers to have safe access to company networks and resources.
Securing IoT Devices:
-
Uses network segmentation and IoT-specific security techniques to defend connected smart devices from security risks.
Network security experts are crucial for protecting businesses from online attacks. They maintain data, prevent unwanted access, ensure availability, maintain privacy, and conform to regulations despite obstacles including changing dangers and resource limitations. They improve company stability through threat detection and response, reputation management, business continuity support, secure remote access, and IoT device security. Professionals with the necessary skills are in greater demand as firms depend increasingly on digital networks. Network security specialists are essential to preserving the security and prosperity of contemporary businesses because they employ vigilance, a multi-layered strategy, and strategic prioritization.
























