Application Security Certifications for Developers and Testers
Discover key application security certifications for developers and testers. Boost your cybersecurity skills with industry-recognized training.

Application security plays a role in the current digital environment for protecting private information and fending off online attacks. By limiting access to information to those who are approved, it protects against unwanted access and upholds data integrity through validation and integrity checks. In addition, effective security measures help firms maintain compliance with laws like GDPR and HIPAA, fight against evolving cyber threats like malware and phishing assaults, and create customer trust by showcasing a dedication to data protection. In an increasingly linked digital world, protecting data, reducing risks, and upholding trust all depend heavily on application security.
To defend against several types of cyber dangers, such as viruses, hacking assaults, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, application security is crucial. Because these dangers are ever-changing, companies must maintain a constant state of alertness and put strong security measures in place to minimize dangers.
Highlight the difficulties and challenges connected with application security.
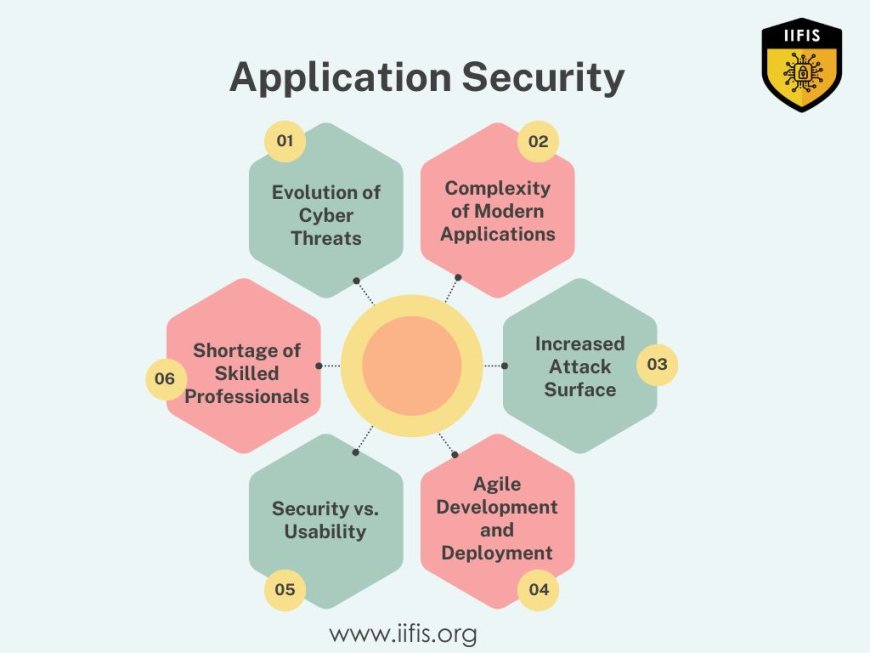
The following are the challenges and issues related to application security in briefly stated:
Evolution of Cyber Threats: Updating security protocols is challenging due to hackers' constantly changing strategies and methods.
Complexity of Modern Applications: Due to the variety of, problems in current technologies can be challenging to identify and mitigate because of code flaws, misconfigurations, and insufficient security protocols.
Increased Attack Surface: The attack surface is increased by interconnected systems, giving hackers more ways to enter networks and compromise data.
Agile Development and Deployment: Agile settings with their fast development cycles run the risk of overlooking or ignoring security as a secondary, which leaves apps exposed.
Security vs. Usability: It is possibly difficult to strike a balance between usability needs and solid security protocols because the former can impede productivity and the latter may impact the user experience.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals: Organizations are finding it difficult to attract and keep people with experience in identifying and mitigating security risks due to a shortage of trained cybersecurity employees.
A complete strategy is needed to address these issues, one that includes keeping up with new dangers, putting in place strong security measures, raising security awareness, and funding cybersecurity talent development.
What is an application security tester?
The following details are provided in point form about an application security tester:
-
Role Definition:
A cybersecurity specialist trained to assess the security of software applications is known as an application security tester.
-
Assessment Techniques:
To find weaknesses in apps, they depend on a variety of strategies including code inspection, automatic scanning, and manual testing.
-
Vulnerability Identification:
To find possible security weaknesses such as input validation mistakes, identity problems, and unsafe setups, application security testers examine the architecture, design, and code of programs.
-
Reporting and Recommendations:
They offer full reports with findings and correction methods when weaknesses are found.
-
Collaboration:
They frequently work together with IT and development teams to improve overall application security and deploy areas.
-
Continuous Learning:
To help organizations stay informed of potential security concerns, application security testers keep up with the latest security best practices and novel dangers. This allows them to keep improving their testing techniques.
Their knowledge is necessary to make sure that, in the modern online environment, apps are safe and resistant to cyberattacks.
What is an application security developer?
The following details are provided in point form regarding an application security developer:
Role Definition:
-
A specialist in cybersecurity with a focus on creating safe software applications is known as an application security developer.
Integration of Security Measures:
-
To create dependable and strong apps, they incorporate security features and controls right into the development process.
Collaboration:
-
Throughout the development lifecycle, application security developers collaborate closely with software engineers and architects to create and implement security solutions.
Secure Coding:
-
To minimize the probability of dangers, they write secure code, use security libraries and frameworks, and conform to secure coding rules.
Security Reviews and Testing:
-
To find and fix any possible weaknesses in the code base, they perform checks for safety and testing using methods including static analysis, dynamic analysis, and penetration testing.
Continuous Learning:
-
Application security developers modify their strategies and protect applications from changing cyber dangers by keeping abreast of the most recent security threats, weaknesses, and best practices.
Their knowledge is necessary for developing software programs that, in the current digital environment, can protect sensitive data and withstand cyberattacks.
Uses of Application Security
Computer systems and software applications depend on application security to defend them from many kinds of attacks and problems. Its main objective is to protect apps from harmful activity, illegal access, and data breaches. Application security has the following important applications:
-
Preventing Data Breaches: Application security features that protect user privacy and lower the risk of hacking include encoding and access controls. These features assist in preventing unwanted access to sensitive data held within apps.
-
Mitigating Cyber Attacks: Application security assists in identifying and preventing cyberattacks, such as malware injections, SQL injections, and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, by adding strong security mechanisms, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, into place.
-
Ensuring Compliance: Organizations are capable of legal and regulatory regulations surrounding data protection and privacy by using application security frameworks and standards, such as the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requirements and the OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) principles.
-
Securing Transactions: Strong application security protects sensitive financial information and stops fraud in e-commerce and financial apps by guaranteeing the integrity and confidentiality of transactions.
-
Protecting Intellectual Property: By limiting illegal access to proprietary software code and digital assets, application security techniques like hidden code and digital rights management (DRM) improve the protection of intellectual property values.
-
Maintaining Business Continuity: Application security reduces the possibility of system interruptions and outages by proactively detecting and fixing security flaws, and providing the ongoing availability of vital company services.
-
Enhancing Customer Trust: By providing users and customers with the assurance that their data is safe and secure, the implementation of strong application security measures improves brand reputation and customer retention.
-
Supporting Secure Development Practices: Application security gives developers the tools they need to create software that is safe and resilient from the ground up. It includes threat modeling, vulnerability assessments, and secure coding techniques.
-
Adapting to Emerging Threats: To effectively minimize new and developing dangers, application security entails keeping up with growing cyber threats and vulnerabilities, implementing proactive safety precautions, and routinely updating security policies.
-
Facilitating Secure Access: To ensure that only those with permission can access sensitive application resources, application security incorporates authentication and authorization technologies like role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Protecting sensitive data and maintaining confidence in internet connections provide constant problems for application security specialists. Testers work in teams to find problems and offer solutions, while developers include security controls throughout the development process. Their combined knowledge ensures that applications are carefully reviewed, reducing the risk of ever-changing cyberattacks. They develop robust apps that can withstand attacks by using secure coding, full reviews, and ongoing learning. Robust application security depends on developers and testers working together to protect sensitive data in an interconnected environment, maintain trust, and provide businesses the confidence to face digital challenges.























