Key Concepts and Frameworks in Application Security Certification
Learn essential concepts and frameworks for application security certification. Explore best practices and strategies to secure your applications.

Application security is becoming increasingly important. Businesses must protect their apps versus possible vulnerabilities because a variety of cyber dangers, such as program and data breaches, are on their way. A security breach can have serious effects, including financial losses, damage to one's reputation, and legal implications.
Companies are taking a proactive approach to application security to tackle these issues. This involves implementing secure coding principles, carrying out frequent security audits, and utilizing cutting-edge technology like access controls and security. Furthermore, conformity to legal regulations like the CCPA and GDPR highlights the necessity of strong security protocols to safeguard confidential information and maintain consumer trust.
The intricate structure of the online environment increases with the advancement of technology, proving the importance of a thorough security program. Applications are deployed across a variety of situations thanks to cloud technology and mobile technology, demanding a proactive approach to security protection. Organizations may reduce risks and maintain trust in an increasingly interconnected world by implementing a complete security strategy.
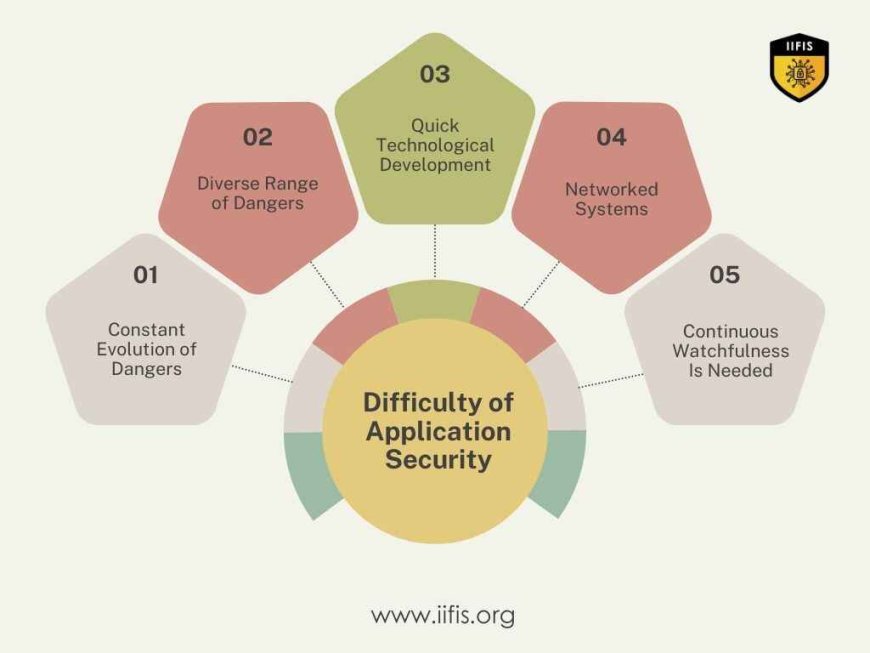
Discuss the difficulty of application security with the changing danger environment.
-
Constant Evolution of Dangers: Security Environment Always Changing: The constantly changing cyber-attack environment provides a challenge to application security. It is hard for companies to stay informed of possible problems since hackers are always improving their methods.
-
Diverse Range of Dangers: Applications are exposed to many different dangers, such as dangerous programs, phishing scams, and data attacks. Since different kinds of attacks must be identified and solved, this diversity makes security efforts more difficult.
-
Quick Technological Development: Technological Innovation Happening Quickly Another problem for application security is the speed at which technology is developing. Modern technologies increase the attack surface, such as cloud computing and IoT devices, so security measures must always be updated to stay functional.
-
Networked Systems: The increasing dependence of modern programs on third-party components and APIs makes security operations more challenging. Systems' connection creates possible dangers that are outside the direct control of an organization, therefore thorough security measures that take into account every component of the system are required.
-
Continuous Watchfulness Is Needed: Organizations must be message keep up with new dangers and have strong safety protocols in place to secure applications and sensitive data. Maintaining security in a dangerous environment that is always changing requires adaptability.
In the dynamic security environment right now, safeguarding apps requires constant attention to detail and flexibility. Organizations can reduce risks by using sound security practices and well-informed decision-making, even in the face of constantly changing online dangers, quick technological developments, and interconnected systems.
What are the key concepts and structures involved in application security certification?
Several fundamental ideas and structures are included in application security certifications regarding the safety and effectiveness of precautions for security. Among the most popular ones are:
-
OWASP Top 10:
The most important safety dangers that online applications face are provided in the commonly implemented Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 foundation. It acts as a fundamental guide for locating and fixing common problems like cross-site scripting, failed verification, and hacking.
-
Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC):
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a methodical approach to software development that incorporates safety requirements at every development stage. Threat modeling, secure coding techniques, code reviews, and security testing are just a few of the tasks it includes to find and fix problems early in the development process.
-
Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS):
A standard methodology called CVSS is used to evaluate the impact of security problems. By giving problems a numerical score based on variables including impact, simplicity of removal, and exploitability, it assists businesses in successfully identifying and addressing security issues.
-
ISO/IEC 27001:
An international standard for information security management systems (ISMS) is ISO/IEC 27001. It offers a thorough framework for creating, putting into practice, keeping up, and continually improving an organization's information security management system, which includes application security-related policies, processes, and controls.
-
NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
The Cybersecurity Standards, created by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), offer guidelines to businesses on how to control and lower cybersecurity risks. Its five primary functions—Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover—assist businesses in properly allocating resources and integrating security activities with business goals.
-
CERT Secure Coding Standards:
To avoid common weaknesses and coding errors, the CERT Safe Coding Standards provide best practices and standards for designing safe code. These standards extend a wide range of programming languages and offer developers practical suggestions on how to reduce security risks when working.
-
PCI DSS:
A set of security guidelines called the Payment Card Information Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) was created to verify that credit card information is handled securely by service providers and retailers. Organizations that handle, store, or transport credit card information must adhere to PCI DSS regulations, which include putting strong application security measures in effect.
Importance of Application Security Certification
The importance of application security certification cannot be clarified. It has important advantages for organizations for the following reasons:
Validation of Competence:
-
A company's ability to execute efficient application safety protocols is proved by certification, which gives stakeholders and clients confidence.
Increasing Credibility:
-
Being certified builds an organization's credibility by informing clients that their data is safe and promoting trust in the company's goods and services.
Regulatory Compliance:
-
By proving compliance with industry requirements through certification, firms can lower their risk of fines and legal repercussions for data security and protection.
Risk Minimization:
-
Certified safety protocols verify that sensitive data is protected against possible weaknesses and reduce the risk of hacking and data leaks.
Advantage of Demand:
-
Achieving certification differentiates businesses from competitors in the industry and attracts customers who value security and compliance.
Application security certification is a must and offers businesses several advantages in protecting their apps and sensitive data. Building trust and confidence among stakeholders and clients can be helped by certification, which verifies competence, improves credibility, maintains regulatory compliance, minimizes risks, and gives one a competitive advantage. Owing to the ever-changing and dynamic nature of cyber-attacks, companies must maintain a state of alertness and adjust to new challenges. To effectively discuss the intricate terrain of application security, they must employ robust security protocols and well-informed decision-making. In an increasingly interconnected world, companies may improve their security posture and sustain a competitive advantage using ongoing improvement and conformity to industry standards and guidelines.























