What Is Information Security?
Information Security protects sensitive information from theft, damage, or unauthorized access, ensuring data stays safe and secure in the digital and physical world

Information security (InfoSec) is all about protecting important information from being accessed, stolen, or damaged by unauthorized people. It ensures that data remains private, accurate, and available when needed. As someone familiar with InfoSec, you know how crucial it is for everyone—whether it's safeguarding personal details, a company’s confidential information, or government data. InfoSec covers key areas like cybersecurity (protecting against hackers), data protection, and risk management to prevent potential threats. In short, infosec plays a vital role in ensuring that our digital world remains safe, secure, and reliable.
Why Should Students Take Information Security Courses?
-
High Demand for Professionals:
-
Organizations need experts to combat evolving cyber threats.
-
Skilled infosec professionals are in short supply, creating lucrative career opportunities.
-
Career Growth Potential:
-
Roles like ethical hacker, penetration tester, and security analyst are in demand.
-
Opportunities for advancement into leadership or specialized positions.
-
Impactful Work:
-
Contribute to protecting critical infrastructure and sensitive data.
-
Play a key role in ensuring privacy and security for individuals and organizations.
-
Bridging the Skills Gap:
-
Address the growing global shortage of cybersecurity experts.
-
Become an indispensable asset to any organization.
-
Personal Empowerment:
-
Equip yourself with knowledge to safeguard personal and professional digital assets.
-
Stay ahead in an increasingly digital landscape.
What Does an Information Security Course Include?
-
Cybersecurity Basics:
-
Introduction to threats, vulnerabilities, and security principles.
-
Understanding confidentiality, integrity, and availability (CIA triad).
-
Network Security:
-
Protecting data as it travels through networks.
-
Tools like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure protocols.
-
Cryptography:
-
Techniques for encrypting data to ensure privacy.
-
Topics include symmetric and asymmetric encryption, digital signatures, and hashing.
-
Risk Management:
-
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks to information systems.
-
Learning to prioritize resources for effective protection.
-
Incident Response:
-
Preparing for and managing security breaches.
-
Strategies for minimizing damage and restoring operations.
-
Ethical Hacking:
-
Offensive security methods to identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
-
Hands-on training in penetration testing tools and techniques.
-
Compliance and Legal Frameworks:
-
Understanding regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
-
Navigating the legal implications of information security.
Types of Information Security Courses
-
Certification Programs:
-
Examples: Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), Certified Information Security Professional.
-
Suitable for beginners and professionals seeking validation of skills.
-
Undergraduate and Graduate Degrees:
-
Comprehensive programs like Bachelor’s in Cybersecurity or Master’s in InfoSec.
-
Provide theoretical knowledge and practical expertise.
-
Online Learning Platforms:
-
Flexible options like Coursera, Udemy, and edX.
-
Often self-paced, allowing for learning alongside work or studies.
-
Bootcamps and Workshops:
-
Short-term, intensive training programs focusing on practical skills.
-
Examples: cybersecurity bootcamps and ethical hacking workshops.
-
Specialized Courses:
-
Advanced topics such as cloud security, forensic analysis, or IoT security.
-
Designed for professionals looking to deepen expertise in specific areas.
Tips for Choosing the Right Course
-
Identify Your Goals:
-
Decide whether you need foundational knowledge or a specialized skill set.
-
Choose courses aligned with desired certifications or career paths.
-
Evaluate Course Content:
-
Ensure the curriculum covers relevant topics like cryptography, ethical hacking, and risk management.
-
Check Accreditation:
-
Select programs offered by reputable institutions or recognized industry bodies.
-
Consider Learning Formats:
-
Opt for in-person, online, or hybrid formats based on your schedule and preferences.
-
Read Reviews:
-
Learn from experiences shared by previous students to gauge course quality.
-
Prioritize hands-on training:
-
Practical experience is crucial—look for courses with labs or real-world projects.
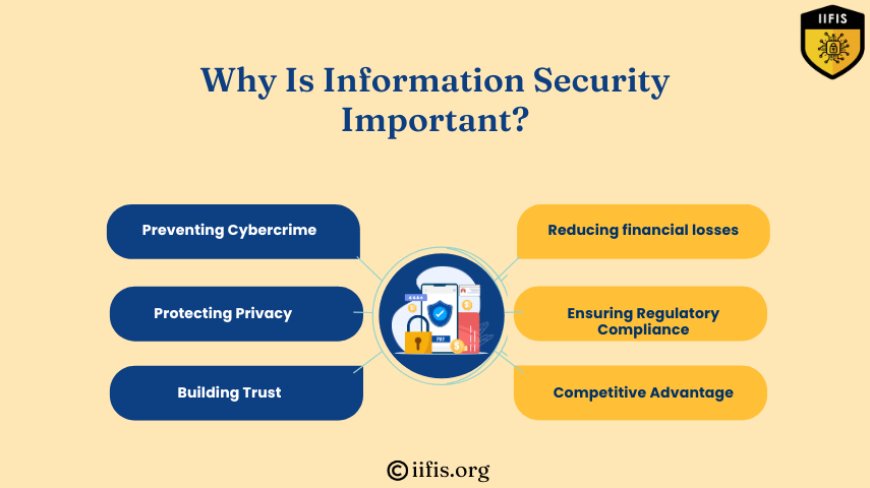
Why Is Information Security Important?
-
Preventing Cybercrime:
-
Safeguards systems and data from malicious attacks like hacking and phishing.
-
Protecting Privacy:
-
Ensures that sensitive personal and organizational information remains confidential.
-
Building Trust:
-
Strengthens consumer and stakeholder confidence in secure systems.
-
Reducing financial losses:
-
Mitigates the economic impact of breaches and data theft.
-
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance:
-
Helps businesses adhere to legal frameworks and avoid penalties.
Tools Used in Information Security
-
Antivirus Software: Detects and removes malware (e.g., Norton, McAfee).
-
Firewalls: Blocks unauthorized access (e.g., Palo Alto Networks, Cisco ASA).
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Monitors for suspicious activities (e.g., Snort, Suricata).
-
Encryption Tools: Secures data through encryption (e.g., VeraCrypt, OpenSSL).
-
Password Managers: Manages secure credentials (e.g., LastPass, Dashlane).
-
Vulnerability scanners: identify system weaknesses (e.g., Nessus, Qualys).
-
Penetration Testing Tools: Tests security defenses (e.g., Metasploit, Burp Suite).
-
SIEM Solutions analyzes security data (e.g., Splunk, IBM QRadar).
-
Forensic Tools: Investigates breaches (e.g., EnCase, FTK).
-
Network Analyzers: Tracks traffic patterns (e.g., Wireshark, SolarWinds).
The Future of Information Security
-
AI in Cybersecurity:
-
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing threat detection and response.
-
Advanced tools can predict and neutralize potential cyberattacks.
-
Cloud Security:
-
As businesses migrate to cloud-based systems, securing these environments becomes critical.
-
IoT Security:
-
The rapid growth of connected devices requires robust security protocols to prevent breaches.
-
Zero Trust Models:
-
Future security strategies will focus on continuous verification instead of perimeter defenses.
-
Enhanced Regulations:
-
Stricter cybersecurity laws will increase the demand for compliance expertise.
-
Education and Awareness:
-
Growing emphasis on training individuals to recognize and mitigate cyber threats.
Information security is an indispensable field in our increasingly digital world. For students, pursuing InfoSec courses offers a gateway to rewarding careers and empowers them to make meaningful contributions to protecting critical information. As technology evolves, the need for skilled professionals in this area will only continue to grow, making InfoSec an excellent choice for anyone looking to thrive in the digital age.























