Evolving Threats and the Role of Cyber Security Certifications
Explore how cyber security certifications help professionals stay ahead of evolving online threats by teaching essential skills and best practices.

Cybersecurity is one of the most important defences against various online dangers. It includes guidelines and devices intended to protect data, networks, and digital systems from opposed and illegal access. cybersecurity is fundamental to maintaining the privacy, availability, and integrity of our digital assets, from private data to important infrastructure.
Given the diverse array of safety risks present in the online environment, the importance of cybersecurity becomes even clearer. Ransomware, fake emails, and programs are just a few of the dangers people and businesses face regularly. Considering the possibility of financial damage, damage to one's reputation, and extensive distractions, it is important to invest in strong cybersecurity protection.
Looking ahead, the importance of cybersecurity will only increase as technology develops and our dependence on digital platforms increases. We can handle the complexity of the online environment with trust and resolve if we promote cybersecurity knowledge, education, and investment. This will make the internet a safer and more secure place for everyone.
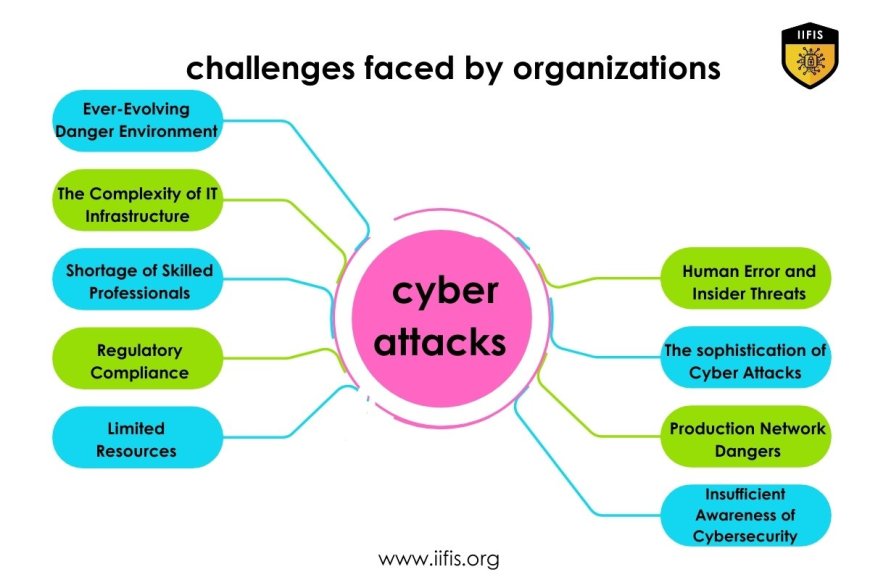
Discussion on the challenges faced by organizations in combating cyber attacks
Ever-Evolving Danger Environment:
-
Organizations find it difficult to stay up to date with the constantly changing environment of cyber threats due to the persistent innovation and strategy modifications of cyber attackers.
The Complexity of IT Infrastructure:
-
With cloud computing, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, networked systems, and complex digital environments, modern businesses function. Because of this complexity, it is challenging to maintain control and visibility, which leaves gaps that cybercriminals might take advantage of.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals:
-
There is an important absence of qualified cybersecurity specialists, which is causing a talent gap in the field. Employers find it difficult to find and keep skilled workers, which makes it more difficult for them to recognize, stop, and respond to cyberattacks.
Regulatory Compliance:
-
Companies have an additional layer of difficulty when it comes to complying with several cybersecurity rules. It can be difficult and resource-intensive to meet regulatory standards while maintaining strong cybersecurity protections.
Limited Resources:
-
Financial limitations and a scarcity of resources for cybersecurity efforts are problems for many companies. Their capacity to invest in cutting-edge security systems, educational programs, and incident response skills is hampered by this limitation.
Human Error and Insider Threats:
-
Human error continues to be a major contributing factor in cybersecurity problems even with advances in technology. Furthermore, insider threats—intentional or not—present a serious risk to data integrity and organizational security.
The sophistication of Cyber Attacks:
-
Cybercriminals use advanced methods, like sophisticated viruses and social engineering strategies, to get above conventional safety precautions. Expertise and advanced cybersecurity solutions are needed to identify and counter these coming attacks.
Production Network Dangers:
-
Complicated supply networks connect organizations, increasing the danger of cybersecurity attacks. Attackers may use network customer or third-party businesses' weaknesses to gain access to target businesses' networks.
Insufficient Awareness of Cybersecurity:
-
Organizational dangers can result from employees' and stakeholders' limited understanding and awareness of issues related to cybersecurity. Creating an environment of security in companies requires the implementation of effective cybersecurity training and awareness campaigns.
Businesses have several difficulties when defending against cyberattacks. A shortage of qualified personnel demanding IT environments, and changing methods of attack are just a few of the challenges facing cybersecurity. Despite these obstacles, resilience can only be improved by proactive investment in cybersecurity measures and awareness campaigns. Making cybersecurity a top priority is crucial for effectively coping with the constantly shifting digital environment.
How can organizations effectively mitigate changing cyber threats?
Organizations can use a multifaceted strategy that includes a range of methods and best practices for successfully avoiding evolving cyber threats:
-
Regular Risk Assessments: Businesses can find possible weak points and dangers to their data and systems by doing periodic risk assessments. Organizations can more efficiently prioritize their mitigation efforts by having a better awareness of their risk environment.
-
Robust Security Measures: Keeping strong security protocols in place, like intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and anti-virus software, aids in defending against regular cyberattacks. Additionally, encryption technologies are essential for shielding private information from attackers.
-
Employee Training and Awareness: Providing cybersecurity best practices training to staff members is crucial for reducing risk from insiders and human error. Topics like password hygiene, phishing awareness, and safe internet browsing practices need to be included in training programs.
-
Patch Management: Updating systems and software with the current security updates improves solving problems that are known to be subject to cyberattacks. Putting in place an organized patch management procedure ensures that the organization's IT infrastructure receives upgrades on time.
-
Network Segmentation: Networks can be divided into smaller, more isolated zones to assist prevent breaches and lessen the impact of cyberattacks. Organizations can lessen the chance of attackers moving laterally by limiting access to critical systems and data.
-
Incident Response Plan: Organizations may react to cyber-attacks quickly and efficiently by creating and testing an incident response plan regularly. Procedures for identifying, containing, and mitigating online dangers should be outlined in this strategy, along with stakeholder communication guidelines.
-
Cooperation and Information Exchange: Operating together and exchanging information with cybersecurity groups and colleagues in the business may provide valuable knowledge about new dangers and practical solutions. By taking part in threat intelligence sharing networks, a company can better protect itself from cyber threats.
-
Continuous Observation and Modification: By getting constant tracking technologies into place, businesses can quickly identify and address online dangers. Organizations can spot problems and reduce risks by keeping a close watch on user behaviour, system activity, and network traffic.
Organizations have to face several obstacles to successfully fight the evolving danger of online crimes, such as a lack of qualified personnel, the strain of complying with regulations, and the increasing technicality of cyberattacks. Organizations can successfully reduce these risks and protect their digital assets, though, by placing proactive steps in place like frequent risk assessments, strong security protocols, employee training, patch management, network segmentation, incident response planning, and promoting relationships within the cybersecurity community. Managing the constantly shifting digital environment and preserving operational continuity require putting cybersecurity first and taking a proactive position.
























