Introduction to Cyber Security Certifications
Explore essential cyber security certifications to boost your career. Learn about top certifications, requirements, and career prospects in this comprehensive guide.

The increase in cyber threats and attacks in today's digital environment has made a critical need for qualified cybersecurity specialists exist. The need for professionals who can protect against cyber attacks has never been higher, as hackers are always changing their strategies and firms are under increasing regulatory pressure. Businesses from a variety of sectors are looking for competent people to secure their digital assets for a variety of reasons, including protecting sensitive data and making sure regulations are followed.
There is a talent shortage in the cyber security industry as a result of this demand surpassing supply. Rising attention is being placed on education and training programs that give people the skills and knowledge they need to close this distance. There are initiatives in place to develop the next generation of cyber security experts who can handle the demands of a world that is becoming more networked, ranging from specialized university programs to online certifications.
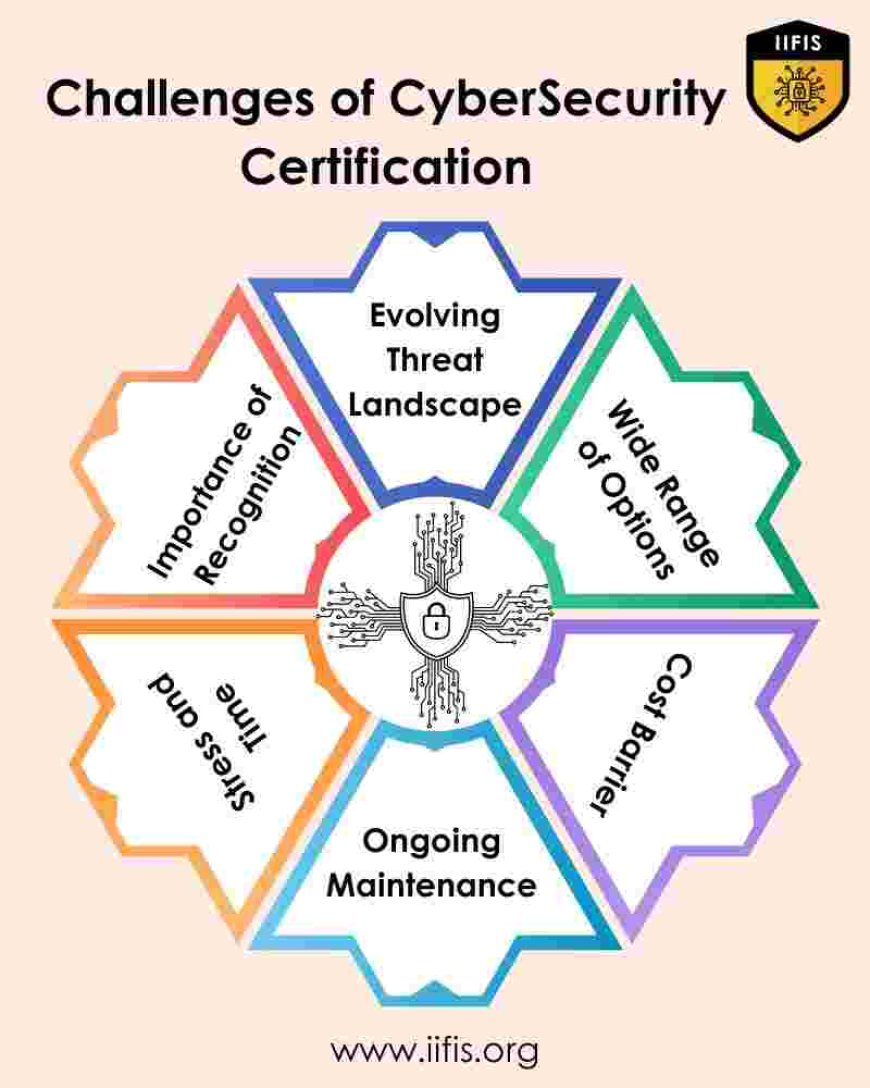
Challenges of Cyber Security Certification
Evolving Threat Landscape:
-
Programs for certification must remain up to date due to the ever-changing nature of cyber-attacks. To confirm that applicants possess the necessary knowledge and skills, course materials and tests must undergo frequent modifications. However, both certification providers and candidates may find this to be a time-consuming and resource-intensive process.
Wide Range of Options:
-
Those attempting to traverse the cybersecurity certification environment may find it difficult to keep up with the multitude of available qualifications. It may be difficult for candidates to determine which certification matches their skill level and professional goals because each one has different requirements and focuses. Delays in obtaining certification may result from this intricacy.
Cost Barrier:
-
Even while certificates in cyber security are useful, many people may find it prohibitively expensive to get them. Exam fees, study materials, and training courses may quickly add up, making certification out of reach for people with no organizational support or financial resources.
Ongoing Maintenance:
-
Getting certified in cyber security is just the first step; continuing to maintain it will take work and money. A lot of qualifications demand you to pass periodic recertification exams or complete continuing education credits. This requires professionals who already manage difficult work schedules and other responsibilities to contribute time and resources.
Stress and Time Commitment:
-
The process of getting ready for and sitting for certification tests can be emotionally and psychologically draining. Candidates frequently have to commit a large amount of time and energy to learning and performing exam objectives, which can negatively impact their general well-being and work-life balance.
Importance of Recognition:
-
Employers may not see every qualification equally when it comes to prestige and recognition. Before devoting time and resources to seeking certification, candidates should carefully assess the certification's industry relevance and reputation. Selecting a globally recognized certification can improve one's credibility and employment opportunities in the cybersecurity industry.
What are the benefits of obtaining cyber security certifications?
-
Enhanced Skills and Knowledge: Candidates pursuing cybersecurity qualifications gain extensive training and expertise in subjects like incident response, network security, and ethical hacking. This gives them the knowledge and skills necessary to identify and mitigate cyber threats.
-
Career Advancement Opportunities: Having a cybersecurity certification might help you grow in the industry and find new job prospects. Candidates who possess the necessary qualifications are frequently given preference by employers since they show a commitment to professional growth and expertise in cybersecurity procedures.
-
Increased Job Marketability: Possessing a cybersecurity certification will help individuals stand out in the competitive job market of today. It acts as concrete proof of their abilities and knowledge, increasing their appeal to companies.
-
Higher Earning Potential: Professionals in cyber security who hold certifications usually earn more money than those who do not. Because workers with recognized certificates have a track record of protecting firms from cyber dangers, employers are ready to pay a premium for them.
-
Global Recognition: Many cybersecurity certifications have gained popularity in the industry and are acknowledged on a global scale. This shows their competence to companies in many locations and industries and allows certified experts to pursue possibilities globally.
-
Professional Credibility: Having a cybersecurity certification improves one's standing and professional credibility in the industry. It shows employers, clients, and employees that they have the abilities and know-how to properly defend against cyberattacks.
-
Networking Opportunities: Professionals frequently network with colleagues and industry experts through certification programs. Within the cyber security field, networking can promote collaboration, knowledge exchange, and professional development.
-
Continuous Learning and Growth: Professionals who want to maintain their cybersecurity certification must keep up with the most recent advancements and industry best practices. This dedication to lifelong learning promotes continued development and applicability in a field that is always changing.
Different Types of Cybersecurity Available
-
Network Security:
The main goal of network security is to avoid malevolent or unwanted access to computer networks. It involves placing safeguards in place for network infrastructure and data transfer, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
-
Endpoint Security:
Protecting specific devices—like PCs, cellphones, and tablets—from online attacks is the main goal of endpoint security. To stop computer problems and unwanted access, this involves setting up device management programs, encryption tools, and antivirus software.
-
Cloud Security:
The goal of cloud security is to safeguard programs and data kept in cloud computing environments. The process includes putting safety protocols in place that maintain the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of cloud-based resources, including encryption, access controls, and identification of risks.
-
Application Security:
Protecting software programs from attacks and flaws is the main goal of application security. This involves setting secure coding principles into place, conducting penetration tests, and reviewing code to stop illegal access, data breaches, and other security dangers.
-
Data Security:
Data security is the process of preventing unwanted access, disclosure, or manipulation of sensitive data. This includes putting access controls in place, protecting information while it's in transit and at rest, and making sure data protection laws like GDPR and HIPAA are followed.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
IAM entails maintaining user identities and limiting resource access according to user roles and permissions. To stop illegal access and identity theft, this involves putting multi-factor identification, single sign-on, and permission control into place.
Cybersecurity certifications are critical for meeting the growing need for skilled workers in the current digital environment. Even though getting and keeping certifications might be difficult, the advantages they provide—such as improved abilities, chances for career progression, and more marketability—make them priceless tools for anybody hoping to succeed in the cybersecurity industry. To safeguard digital assets, maintain regulatory compliance, and minimize risks, trained personnel are crucial as businesses and organizations struggle with constantly changing cyber dangers. People can invest in education, training, and certification programs to get the skills necessary to meet the demands of a constantly evolving cybersecurity environment and help create a more secure and safe online environment.
























