The Information Security Certification Explained
Learn about Information Security Certification: its benefits, types, and requirements. Understand how to become certified and get insights into the process with "The Information Security Certification Explained.

Information security certifications are important in the modern era of technology for verifying experts' know-how and reliability when it involves protecting digital assets from ever-changing cyber threats. It can be hard to understand the vast array of available certification choices, ranging from entry-level credentials like CompTIA Security+ to expert certifications like CISSP and CEH. However, aspirant cybersecurity professionals can design their route to success by understanding the significance of certificates, investigating their possibilities, and matching certification courses with personal interests and career goals.
It is important to carefully analyze a variety of criteria while selecting a certification path, including skill level, professional goals, industry needs, and personal interests. People can position themselves as reliable experts in the ever-evolving field of information security and improve their marketability by utilizing useful advice and techniques for exam preparation, ongoing education, and professional development. Each certification milestone advances individuals toward their career objectives and helps them make an important difference in the security of the digital world via hard work and devotion.
The challenge of Choosing the Right Information Security Certification for Career Path
-
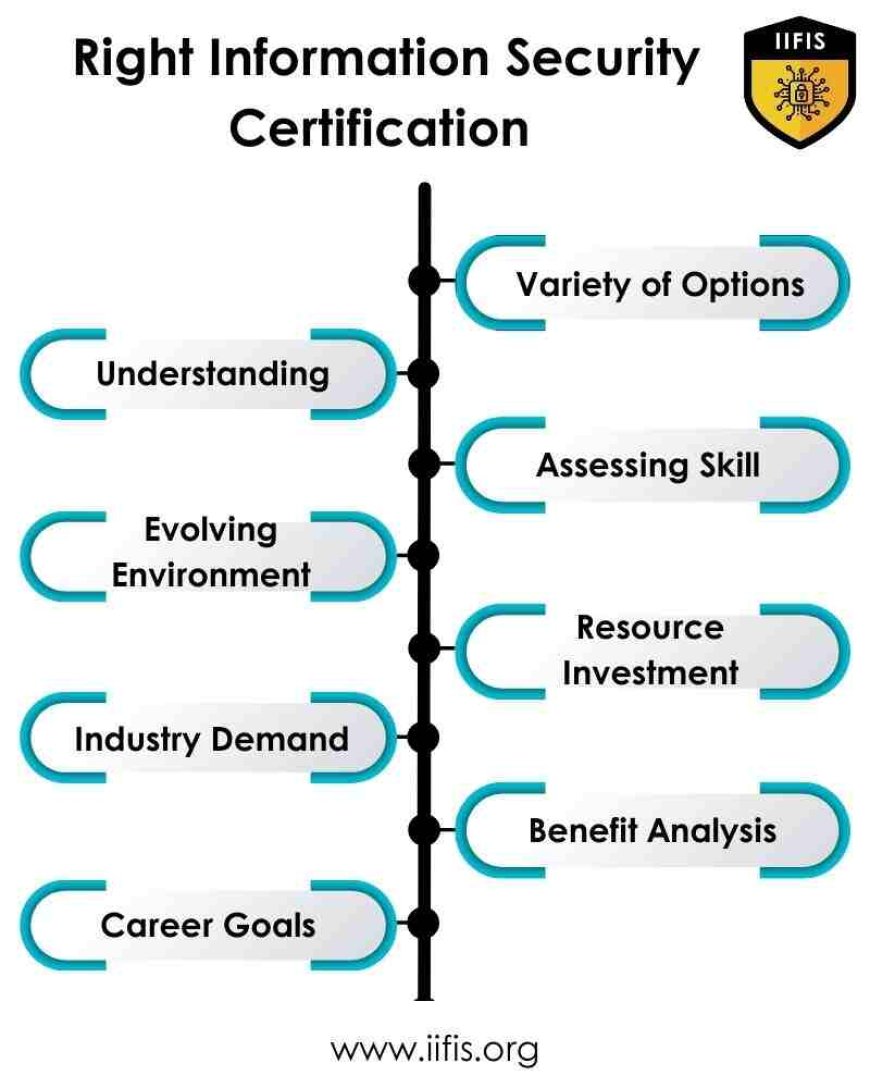
Variety of Options:
It can be difficult to identify which information security certification best suits your dreams and career goals due to the deluge of options available.
-
Understanding Differences:
Research is necessary to understand how each certification relates to your intended career path in information security because everyone covers a different set of topics and skills.
-
Assessing Skill:
Choosing the right certification depends on assessing your current cybersecurity knowledge and experience. Professionals with experience can pursue advanced qualifications like CISSP or CEH, while beginners can choose core certifications like CompTIA Security+.
-
Evolving Environment:
Because new certifications are created to address challenges and new technologies, the certification environment is always changing. It can be impossible to keep up with these developments and to know which qualifications employers value.
-
Resource Investment:
Obtaining a certification is a major time, financial, and human commitment. Before committing to a certification, factors including exam costs, study materials, and preparation time should be taken into account.
-
Industry Demand:
It's critical to comprehend the need for particular qualifications in your business or desired career role. Examining job advertisements and conversing with professionals in the field can offer valuable perspectives on the certifications that companies highly regard.
-
Cost-Benefit Analysis:
It's critical to consider both the financial and professional advantages of earning a certification. Take into account elements like pay raises, employment prospects, and professional growth.
-
Alignment with Career Goals:
In the end, carefully weighing your professional objectives, passions, and aspirations is necessary while selecting the appropriate information security certification. You may make sure that your certification is a useful tool for developing your information security profession by matching it with your long-term goals.
What are the different levels of information security certifications?
-
Entry-Level Information Security Certifications: These certifications offer fundamental knowledge and abilities and are intended for individuals who are new to the subject of information security. They act as a starting point for anyone wanting to pursue a cybersecurity career. CompTIA Security+ and Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate are two examples.
-
Intermediate Information Security Certifications: Professionals looking to further their expertise in information security and have some experience may think about pursuing intermediate-level certifications. These certificates need a strong grasp of foundational principles and go further into certain cybersecurity topics. The Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) are two examples.
-
Advanced Information Security Certifications: Advanced certificates are meant for seasoned workers who want to prove that they are information security experts. These certifications cover complicated subjects in cybersecurity strategy, management, and implementation and call for a high level of competence. The Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP) and the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) are two examples.
-
Specialized Information Security Certifications: Professionals with specific interests or paths to employment are catered to with specialized certificates that concentrate on specific topics within information security. They offer in-depth instruction and specialized knowledge in fields including digital forensics, cloud security, and ethical hacking. The Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) and Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) are two examples.
-
Vendor-Specific Information Security Certifications: Technology businesses offer vendor-specific certifications to verify expertise in their platforms or products. These credentials are pertinent for professionals using those items and are geared toward particular technology or solutions. Certifications from companies such as Cisco, Microsoft, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) are a few examples.
Ethical Considerations in Information Security Certification
Ethical Hacking Practices:
-
Certain certificates, like the Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), concentrate on methods related to ethical hacking. These certifications place a strong emphasis on the value of applying hacking skills for good intentions rather than evil ones, such as finding flaws and improving security protocols.
Responsible Disclosure:
-
The idea of responsible disclosure—which advocates for professionals to responsibly and ethically notify pertinent stakeholders about security vulnerabilities—is frequently promoted by information security certifications. This helps stop bad people from using bugs for their gain and enables businesses to quickly fix security flaws.
Confidentiality and Privacy:
-
Respecting privacy and confidentiality rights is one of the ethical factors taken into account in information security certifications. It is required of certified experts to handle confidential data carefully, making sure that it is shielded from unwanted access and disclosure.
Integrity and Honesty:
-
When it comes to information security certification, honesty and integrity are essential ethical concepts. When interacting with clients, coworkers, and the general public, certified professionals are required to conduct themselves with honesty, integrity, and openness. This entails upholding professional norms of behavior, following ethical codes of conduct, and truthfully advertising their qualifications.
Avoiding Conflict of Interest:
-
Candidates seeking information security certifications are frequently obliged to declare any potential conflicts of interest that can compromise their objectivity or impartiality. This provides that qualified professionals may prioritize the needs of their clients or employers while carrying out their obligations impartially and without bias.
Compliance with Laws and Regulations:
-
Information security methods are governed by laws, regulations, and industry standards, which certified experts are expected to follow. This entails abiding by the legal and regulatory obligations for cybersecurity, privacy, and data protection in addition to the ethical standards set forth by professional associations and certification authorities.
Continuous Learning and Professional Development:
-
A commitment to lifelong learning and professional development is also a matter of ethics. To remain competent and productive in the sector, certified experts are urged to stay current on new threats, technological advancements, and ethical standards in information security.
Information security certifications attest to a professional's proficiency in safeguarding digital assets. Understanding ethical responsibilities and matching courses to job objectives are fundamental for navigating the varied certification environment. Selecting the appropriate certification requires evaluating one's skills, interests, and the demands of the sector. Integrity in cybersecurity practice is maintained by ethical factors such as law-abiding behavior and ethical hacking. Professional achievements are symbolized by certifications, which enable people to positively influence digital security. Through their commitment and ongoing education, credentialed experts are essential in protecting society and organizations from cyber threats.