What is Cyber Security And Different Types Of Cyber Security?
Learn what cybersecurity is and explore its key types, including network, application, and cloud security, to protect data and systems from cyber threats.

In our increasingly connected world, cybersecurity has become more important than ever. With the constant rise of cyber threats, it's essential to protect systems, networks, and sensitive data from online attacks, unauthorized access, and theft. Cybersecurity involves a wide range of practices, tools, and technologies designed to safeguard digital assets from the ever-growing threat of cybercriminals. As cyberattacks become more advanced, having strong cybersecurity measures in place is crucial for both individuals and organizations to prevent significant damage and loss.
What is cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and digital attacks. It involves using advanced technologies, frameworks, and best practices to safeguard information from hackers, malware, ransomware, and other online dangers.
Effective cybersecurity measures ensure that sensitive data remains confidential, intact, and available only to authorized users. Without proper security, organizations risk losing valuable information, facing financial losses, and damaging their reputation.
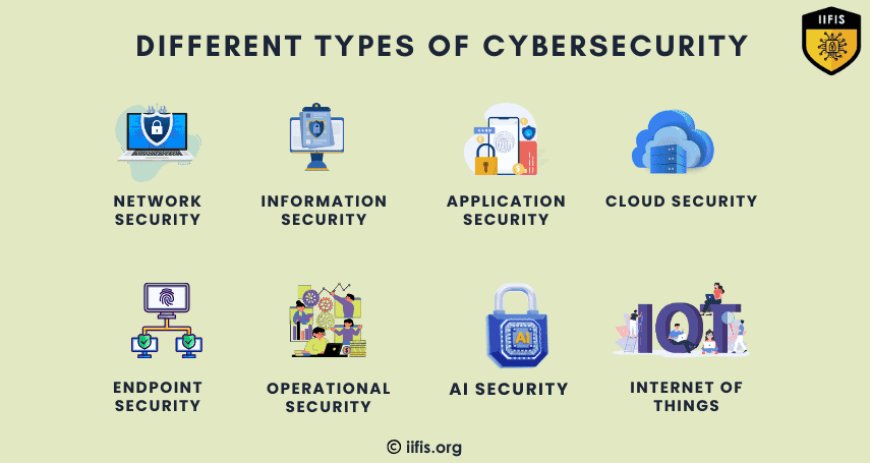
The Different Types of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity isn’t just about installing antivirus software; it covers multiple aspects of digital security. Here are the main types of cybersecurity:
Network Security
Network security focuses on protecting computer networks from cyber threats like unauthorized access, hacking, and data breaches. Since networks are a prime target for cybercriminals, organizations use various tools and protocols, such as:
-
Firewalls: act as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks, monitoring incoming and outgoing traffic.
-
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Detects and alerts suspicious activities within the network.
-
Virtual private networks (VPNs) encrypt internet connections to ensure secure data transmission.
With businesses increasingly depending on remote work, network security has become more crucial than ever.
Information Security (InfoSec)
Information security focuses on protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access, modification, or destruction. It ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Key techniques include:
-
Encryption: Converts data into unreadable formats, preventing unauthorized access.
-
Access Controls: Restricts who can view or modify specific information.
-
Data Masking: Hides sensitive information from unauthorized users.
This type of cybersecurity is essential for protecting customer data, financial records, and confidential business information.
Application Security
Application security ensures that software applications are protected from vulnerabilities and cyber threats. Hackers often exploit weaknesses in applications to gain unauthorized access. Security measures include:
-
Secure Coding Practices: Writing software code that is resistant to attacks.
-
Firewalls for Applications: Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) help filter and monitor HTTP requests.
-
Regular Updates and Patches: fixing known vulnerabilities to prevent exploitation.
With the rise of mobile and web applications, securing apps is essential to prevent data breaches.
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data stored on cloud platforms from cyber threats. Since more businesses are moving to cloud computing, securing cloud environments is critical. Common cloud security measures include:
-
Encryption of Cloud Data: Ensuring data remains secure even if intercepted.
-
Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controlling user access to cloud resources.
-
Secure Cloud Configurations: Preventing misconfigurations that can expose sensitive data.
Cloud security ensures that businesses can use cloud services without compromising on security.
Endpoint Security
Endpoint security focuses on securing devices like computers, mobile phones, and tablets. Since employees access business systems from various locations, securing endpoints is essential. Key solutions include:
-
Antivirus and Anti-malware Software: Protects devices from malicious attacks.
-
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Monitors endpoints for suspicious activities.
-
Mobile Device Management (MDM): Ensures security policies are applied to mobile devices.
Without endpoint security, hackers can exploit unsecured devices to gain access to networks.
Operational Security (OpSec)
Operational security focuses on protecting internal business processes and decision-making from cyber threats. It involves:
-
Monitoring Employee Access: Ensuring only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
-
Security Awareness Training: Educating employees about potential cyber threats.
-
Incident Response Plans: preparing strategies to handle security breaches effectively.
Organizations that prioritize operational security minimize risks related to insider threats and human errors.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM ensures that only authorized individuals can access critical systems and data. It prevents unauthorized access through methods like:
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Requiring multiple verification methods for secure login.
-
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigning access privileges based on job roles.
-
Biometric authentication: using fingerprints or facial recognition for identity verification.
IAM plays a vital role in preventing identity theft and unauthorized access.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cybersecurity isn’t just about prevention; it’s also about recovery. Disaster recovery and business continuity ensure that organizations can quickly recover from cyberattacks or system failures. Key aspects include:
-
Regular Data Backups: Ensuring critical data is backed up and retrievable.
-
Disaster Recovery Plans: Having a strategy in place to restore operations after an attack.
-
Incident Response Teams: Experts who handle security breaches effectively.
A strong recovery plan minimizes downtime and business disruptions.
Internet of Things (IoT) Security
IoT security focuses on protecting smart devices, such as smart home systems, industrial sensors, and connected vehicles. Cybercriminals often target IoT devices due to weak security. Security measures include:
-
Secure Firmware Updates: Keeping IoT software up to date.
-
Network Segmentation: Separating IoT devices from critical networks.
-
Strong authentication: ensuring only authorized users can control IoT devices.
As IoT devices become more common, securing them is crucial to preventing cyberattacks.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Security
With the rise of AI and machine learning, cybersecurity must also evolve. AI security focuses on protecting AI models from attacks that manipulate or exploit algorithms. Strategies include:
-
Adversarial Training: Training AI models to recognize and resist attacks.
-
AI Monitoring: Detecting anomalies in AI-driven systems.
-
Ethical AI Practices: Ensuring AI models are designed securely and fairly.
As AI becomes integrated into cybersecurity, it can help in detecting and preventing threats more effectively.
Cybersecurity isn’t just about antivirus software; it’s about using multiple layers of protection for all your systems and data. As technology keeps changing, having strong, adaptable security is more important than ever. By staying ahead of new threats, we can protect our data, keep businesses running smoothly, and create a safer online space for everyone.